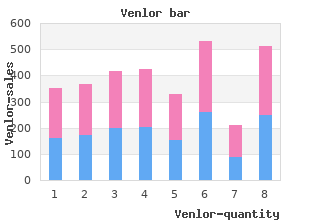
Venlor
"Buy venlor 75 mg free shipping, anxiety symptoms lump in throat."
By: Bertram G. Katzung MD, PhD
- Professor Emeritus, Department of Cellular & Molecular Pharmacology, University of California, San Francisco

http://cmp.ucsf.edu/faculty/bertram-katzung
Tese feet are not abnormal as they can easily be turned into a normal position by gentle pressure buy 75mg venlor visa anxiety questionnaire pdf. Some infants have one or both feet which are twisted inward and cannot be turned into a normal position order venlor 75mg without prescription anxiety questions. The cause may be familial or due to oligohydramnios (pressure on feet during pregnancy 75mg venlor with amex anxiety 9gag gif. Tese infants must be referred to an orthopaedic clinic within a few days of delivery purchase venlor 75mg line anxiety symptoms jaw, as early treatment with strapping or serial plaster of Paris casts can correct the abnormality. Without correct treatment, clubbed feet result in permanent deformity and crippling. At birth the upper end of an infant�s femur (the femoral head) is normally in the hip joint and cannot be pushed out (dislocated. If the hip is dislocatable then the femoral head can easily be moved out of the joint. The hips of all infants should be examined at birth (Barlow�s test) to detect either a dislocated or dislocatable joint. If the early diagnosis is missed, the infant may start to walk late and will have an abnormal waddling gait. If a hip is dislocated, then the infant must be referred to an orthopaedic clinic at a level 2 or 3 hospital for treatment within a few days of delivery. Once the clinical diagnosis is confrmed with an X-ray or by ultrasonography, the infant�s legs should be placed in a plaster of Paris splint. With the correct, early treatment most children with a dislocated hip will walk normally although arthritis in adult life is common. If the hip is only dislocatable, the infant should be examined again afer 2 weeks. However, most dislocatable hips return to normal within 2 weeks and need no further treatment. If a testis is not in the scrotum and cannot be gently pushed into the scrotum, then it is undescended. Many undescended testes will move into the scrotum spontaneously during the frst 3 months. With bilateral undescended testes, an earlier operation is important to reduce the risk of infertility. All undescended testes have an increased risk of malignancy in adulthood even if they were corrected in infancy. If the opening is on the underside of the penis or at the base of the scrotum, then the infant has hypospadias. Tese infants also have a curved rather than a straight penis and at birth appear to have been partially circumcised. It is important to refer these infants to a urological clinic within a few weeks of birth. Tese infants must not be circumcised as the foreskin may be needed to correct the urethra. It is important to reassure the parents that the abnormality can be corrected and that the infant�s sexual function will be normal when he grows up. Ambiguous genitalia means that the external sex organs are not typically male or female. They should all be referred urgently to a level 3 hospital for investigation, as one of the common causes of ambiguous genitalia results in a lack of important adrenal hormones that may cause hypoglycaemia and dangerous changes in the serum sodium and potassium concentrations. Normally the inguinal canal closes afer the testes have descended into the scrotum at about 36 weeks of gestation. However, if the canal does not close normally, bowel will push (herniated) into the scrotum resulting in an inguinal hernia. The mass may be frm or sof, ofen changes in size as the bowel moves in and out of the scrotum, and usually becomes bigger when the infant cries. The danger of an inguinal hernia is that the bowel may become trapped (incarcerated) in the scrotum. This will cut of the blood supply to that portion of the gut resulting in bowel obstruction, death of the bowel wall (gangrene) and perforation. To prevent this complication, inguinal hernias should be repaired when the infant is well enough to have a general anaesthetic and weighs more than 2500 g. This is an inguinal hernia where the opening from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum is only big enough to allow through fuid but not bowel (hydrocoeles. Like an inguinal hernia, it also presents as a one-sided or bilateral scrotal swelling. However, the scrotum transilluminates very well (the scrotum lights up if a torch is held against it. However, some fuid hernias, especially if they are very big, do not disappear and require surgical correction at about 3 months. A birth mark (a naevus) is a mark on the skin at or soon afer birth caused by increased pigment or an abnormal collection of blood vessels. About 10% of infants have 1 or more raised, red marks on the skin which appear in the frst few weeks of life. Tese are known as �strawberry marks� and are formed by an abnormal collection of large veins. This is known as a �port wine stain� and is formed by an abnormal collection of small veins. It is due to excessive pigment cells and, therefore, does not change colour when pressed. When these children are older the area of afected skin should be removed by a plastic surgeon as this birth mark can become malignant in adulthood. If the infant has a single umbilical artery, there is a much higher than normal chance that the infant also has other birth defects.
The purpose of transfusion of blood products is to replace coagulation factors and red blood cells for oxygen carrying capacity venlor 75mg without prescription anxiety 8dpo, not for volume replacement discount venlor 75mg without prescription anxiety symptoms for no reason. To avoid dilutional coagulopathy generic 75mg venlor fast delivery anxiety keeping you awake, concurrent replacement with coagulation factors and platelets may be necessary purchase 75mg venlor free shipping anxiety symptoms heart rate. Accurate pregnancy dating is critical to the diagnosis (see also �Estimated Date of Delivery� in Chapter 5. Accurate assessment of gestational age and diagnosis of postterm gestation, as well as recognition and management of risk factors, may reduce the risk of adverse sequelae. Fetal risks include an increased perinatal mortality rate, uteroplacental insuf ficiency, meconium aspiration, intrauterine infection, low umbilical artery pH 256 Guidelines for Perinatal Care levels at delivery, and low 5-minute Apgar scores. Significant risks to the preg nant woman include an increase in labor dystocia, an increase in severe perineal injury related to macrosomia, and a doubling in the rate of cesarean delivery. Management Many authorities recommend prompt delivery in a postterm patient with a favorable cervix and no other complications. Although postterm pregnancy is defined as a pregnancy of 42 weeks or more of gestation, data suggest that rou tine induction at 41 weeks of gestation has fetal benefit without incurring the additional maternal risks of a higher rate of cesarean delivery. Women with postterm gestations who have unfavorable cervices can either be managed expectantly or undergo labor induction. Many practitioners use twice-weekly testing with some evaluation of amniotic fluid volume beginning at 41 weeks of gestation. Delivery should be initiated if there is evidence of fetal compromise or oligohydramnios. Preterm Birth ^158^241 Preterm birth is defined as birth before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Spontaneous preterm birth includes preterm labor, preterm spontaneous rup ture of membranes, and cervical insufficiency. Preterm birth is the leading cause of neonatal mortality and one of the most common reasons for antenatal hospitalization. In the United States, approximately 12% of all live births occur before term, and preterm labor preceded approximately 50% of these preterm births. The pathophysiologic events that trigger preterm parturition are largely unknown but may include decidual hemorrhage (abruption), mechanical fac tors (uterine overdistention or cervical incompetence), hormonal changes (per haps mediated by fetal or maternal stress), infection, and inflammation. Risk Factor Identification and Management A prior preterm birth is commonly reported to confer a 1. Other risk factors for preterm birth Obstetric and Medical Complications 257 include African American race, age younger than 17 years or older than 35 years, low socioeconomic status, underweight prepregnancy body mass index, smoking, vaginal bleeding in more than one trimester, bacterial infections, and short cervical length. Screening for risk of preterm birth by means other than his toric risk factors is not beneficial in the general obstetric population. Fetal fibronectin testing may be useful in women with symptoms of preterm labor to identify those with negative values and a reduced risk of preterm birth, thereby avoiding unnecessary intervention. Women with a singleton gestation and prior spontaneous pre term birth should be offered progesterone supplementation starting at 16 weeks of gestation to reduce the risk of the recurrence of preterm birth. Diagnosis of Preterm Labor the diagnosis of preterm labor is generally based upon clinical criteria of regular uterine contractions accompanied by cervical dilation, or effacement or presen tation, or both with regular contractions and at least 2 cm dilation. Fewer than 10% of women with the clinical diagnosis of preterm labor actually deliver within 7 days of presentation. It is important to recognize that preterm labor is not the only cause of preterm birth; numerous preterm births are preceded by either rupture of membranes (see also �Premature Rupture of Membranes� later in this chapter) or other medical problems. Patients with suspected preterm labor should be examined and observed for 1�2 hours, have their uterine activity monitored, and undergo serial cervi cal examinations to document the presence or absence of cervical change. The positive predictive value of a positive fetal fibronectin test result or a short cer vix alone is poor and should not be used exclusively to direct management in the setting of acute symptoms. Because preterm labor often is associated with urinary tract infections, a dipstick or a microscopic examination of urine and urine culture may be helpful. Ultrasound examination also may be considered to confirm gestational age, to estimate fetal weight in order to receive appro priate counseling from pediatrics, and to assess the presence of any congenital anomalies. Management of Preterm Labor Interventions to reduce the likelihood of delivery should be reserved for women likely to give birth and who are at a gestational age at which delay in delivery 258 Guidelines for Perinatal Care will provide benefit to the newborn. Historically, nonpharmacologic treatments to prevent preterm births in women who have preterm labor have included bed rest, abstention from intercourse and orgasm, and hydration. Evidence for the effectiveness of these interventions is lacking, and adverse effects have been reported. Proposed pharmacologic interventions to prolong pregnancy include tocolytic drugs to inhibit uterine contractions and antibiotics to treat intrauter ine bacterial infection. Therapeutics agents associated with improved neonatal outcomes include antenatal corticosteroids for fetal maturation and magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection. Evidence supports the use of first-line tocolytic treatment with beta-mimetics, calcium channel blockers, or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs for short-term prolongation of pregnancy (up to 48 hours) to allow for the administration of antenatal steroids. Maintenance therapy with tocolyt ics has been ineffective for preventing preterm birth and improving neonatal outcomes and, therefore, is not recommended for this purpose. Tocolysis is contraindicated when the maternal and fetal risks of prolonging pregnancy or the risks associated with these drugs are greater than the risks associated with preterm birth. Antibiotic use intended only for pregnancy prolongation in women with preterm labor with intact membranes does not have short-term neonatal benefits and may be associated with long-term harm. Thus, antibiotics should not be used for this indication in women with preterm labor and intact mem branes. The most beneficial intervention for improvement of neonatal outcome in patients who deliver preterm is the administration of antenatal corticosteroids. A single course of corticosteroids is recommended for pregnant women between 24 weeks and 34 weeks of gestation who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days (see also �Assessment and Management of Fetal Pulmonary Maturation� earlier in this chapter. The available evidence suggests that magnesium sulfate given before anticipated early preterm birth reduces the risk of cerebral palsy in surviving infants if administered when birth is anticipated before 32 weeks Obstetric and Medical Complications 259 of gestation. Hospitals electing to use magnesium sulfate for fetal neuroprotec tion should develop uniform and specific guidelines regarding inclusion crite ria, treatment regimens, concurrent tocolysis, and monitoring in accordance with one of the larger trials.
Mechanical Insufflator-Exsufflator � Most effective method of mechanical assistance for secretion clearance in paralyzed patients buy discount venlor 75mg on-line anxiety scale. Use Noninvasive Ventilation � Mechanically assisted ventilation provides respiratory muscle rest venlor 75 mg overnight delivery 0503 anxiety and mood disorders quiz, decreasing the energy expenditure of the respiratory muscles discount 75 mg venlor anxiety symptoms throat. Positive Pressure Body Ventilators � Provide positive pressure on the abdomen to assist diaphragmatic cephalad movement purchase 75 mg venlor overnight delivery anxiety symptoms 8dp5dt, promoting expiration. When deflated, the diaphragm and the abdominal contents fall to resting position, resulting in passive inspiration. A trunk angle of 75� from the horizontal is optimal but may be used with 45� in some cases. Inspiration may be supplemented by the use of available inspiratory muscles and or glossopharyngeal breathing. Negative and Positive Pressure Body Ventilator � Rocking Bed � Rocks the patient along a vertical axis (15�30 degrees from the horizontal) utilizing the force of gravity to assist ventilation. Cephalad movement of the abdomi nal contents pushes the diaphragm up with production of positive pressure. Negative Pressure Ventilators � Create intermittent extrathoracic pressure over the chest wall and abdomen, helping inspiration. A negative pressure ventilator creates subatmo spheric pressure under the grid and wrap. Uses: in patients with scoliosis or with sensory deficits Disadvantages: difficult to don, decreased access to the body by the medical personnel; dif ficult to turn the patient � Cuirass or Chest Shell Ventilators � Firm shell that covers the chest and abdomen attached to a negative pressure ventilator that generates a subatmospheric pressure under the shell. Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tubes � Cuffed Tracheostomy Tube � Provides a good air seal, protects lower airways from aspiration, and prevents air leak ing through the upper airway. Non-Fenestrated Tracheostomy Tubes � Fenestrated Tubes � Good for patients who are able speak and require only intermittent ventilatory assistance � A continuous inner cannula can be used with an outer fenestrated cannula. The fenestra tions should lie within the lumen of the trachea and should not touch the tracheal wall (may develop granulation tissue around the holes and become clogged with secretions. If the patient wants to talk, a one-way talking valve may be used on the tracheos tomy tube. These devices open on inhalation and close during exhalation to produce phonation. Speaking Valves � Speaking tracheostomy tubes (eg, Portex �Talk� tube, Bivona Fome-cuff with side-port airway connector, Communi-trach) � Used in alert and motivated patients, who require an inflated cuff for ventilation and who have intact vocal cords and the ability to mouth words. Patients need to speak short sentences (because constant flow through the vocal cords can cause the voice to fade away. Creates #007 for ventilator positive closure feature use (only valve for ventilator) Montgomery One-way valve Fits standard 15-mm Silicone membrane is hinged; (Boston Medical hub or Boston cannula maintains open position Products, Inc. Special cough release feature Trachoe (Boston Two types of Tracheostomy tube Tracheostomy tube is Medical Products, fenestrated inner with attachment which modified by the placement Inc. Closes upon and can be attached expiration to direct air into to T-piece the upper airway Hood Laboratories One-way valve Fits standard 15-mm Valve contains a ball which hub moves, opening upon inspiration and closing upon exhalation * All valves must be used with deflated tracheostomy tube cuffs. Communication and Swallowing Management of Tracheostomized and Ventilator-dependent Adults. The cuffless trach is down sized to a smaller size and the patient evaluated for ability to cough secretions. When plugged, the patient may breathe through the upper airway without resistance from the tracheostomy tube. Diaphragmatic Pacer � Another means of invasive ventilatory support is electrophrenic respiration with the use of a diaphragmatic pacer, in patients with intact phrenic nerves and diaphragm. A decrease in dietary saturated fats and cholesterol may improve lipoprotein levels. Both behavior modifi cation and the addition of lipid lowering medications are proven to be beneficial in combination. The intermediate stage follows immediate outpa tient cardiac rehabilitation when the patient is not intensely monitored and/or supervised but is still involved in regular endurance exercise training and lifestyle change. It represents the work of the peripheral skeletal muscles rather than myocardial muscles. It is usually expressed in the millimeters of O2 consumed per kilogram of body weight per minute. As a result, stroke volume will increase during the next contraction when venous return is increased. This process is known as the Frank-Starling mechanism (or Stanley�s law of the heart. It enables the heart to eject the additional venous return, thereby increasing stroke volume. Increased venous filling rate and stroke volume: increased venous return increases the ventricular filling (end-diastolic volume) and therefore preload, which is the initial stretch ing of the cardiac myocyte prior to contraction. Myocyte stretching increases the sarcomere length, which causes an increase in force generation. This mechanism enables the heart to eject the additional venous return, thereby increasing stroke volume. Exercise training as a sole inter vention has not affected consistent improvement in lipid profiles. Optimal lipid management requires specifically directed dietary and, when medically indicated, pharmacological man agement as a component of multifactorial cardiac rehabilitation program. Reduction of Cigarette Smoking Education, counseling, and behavioral intervention are beneficial for smoking cessation dur ing cardiac rehab. Improvement in Psychosocial Well-Being and Stress Reduction Improvement in psychological status and functioning, including measures of emotional stress and reduction of the Type A behavior pattern. Reduction in Mortality Multifactorial cardiac rehabilitation service can reduce cardiovascular mortality in patients following myocardial infarction.
In such circumstances trusted venlor 75 mg anxiety symptoms even on medication, transfer to a facility with a higher level of perinatal care may be appropriate purchase 75mg venlor visa anxiety symptoms gad. An infant cheap 75mg venlor free shipping anxiety symptoms questionnaire, whose mother was unable to be transferred before delivery venlor 75 mg sale anxiety effects on the body, usually should be transferred after stabilization of the mother following delivery (see also Chapter 4, �Maternal and Neonatal Interhospital Transfer�. Capabilities of Health Care Providers in Hospitals Delivering Basic, Specialty, and Subspecialty Perinatal Care* ^ Level of Care Capabilities Health Care Provider Types Basic Surveillance and care of all Family physicians, obstetricians, patients admitted to the obstetric laborists, hospitalists, certified service, with an established triage nurse�midwives, certified midwives, system for identifying patients at nurse practitioners, advanced high risk who should be transferred practice registered nurses, to a facility that provides specialty physician assistants, surgical or subspecialty care assistants, anesthesiologists, and Proper detection and initial care radiologists of unanticipated maternal�fetal problems that occur during labor and delivery Capability to begin an emergency cesarean delivery within an interval based on the timing that best incorporates maternal and fetal risks and benefits Availability of appropriate anesthesia, radiology, ultrason ography, and laboratory and blood bank services on a 24-hour basis Care of postpartum conditions Ability to make transfer arrange ments in consultation with physicians at higher level receiving hospitals Provision of accommodations and policies that allow families, including their other children, to be together in the hospital following the birth of an infant Data collection, storage, and retrieval Initiation of quality improvement programs, including efforts to maximize patient safety Specialty Provision of all basic care services All basic health care providers, plus care of appropriate women at plus sometimes maternal�fetal high risk and fetuses, both admitted medicine specialists and transferred from other facilities Subspecialty Provision of all basic and specialty All specialty health care providers, care services, plus evaluation of plus maternal�fetal medicine new technologies and therapies specialists (continued) Organization of Perinatal Health Care 11 Table 1-2. Capabilities of Health Care Providers in Hospitals Delivering Basic, Specialty, and Subspecialty Perinatal Care* (continued) Level of Care Capabilities Health Care Provider Types Regional Provision of comprehensive perinatal All subspecialty health care subspecialty health care services at and above providers, plus other subspecialists, perinatal health those of subspecialty care facilities. Definitions, Capabilities, and Health Care Provider Types: Neonatal Levels of Care* ^9^13^14^78 Level of Care Capabilities Health Care Provider Types� Level I well Provide neonatal resuscitation Pediatricians, family physicians, newborn at every delivery nurse practitioners, and other nursery Evaluate and provide postnatal advanced practice registered care to stable term newborn infants nurses Stabilize and provide care for infants born at 35�37 weeks of gestation who remain physiologically stable Stabilize newborn infants who are ill and those born before 35 weeks of gestation until transfer to a higher level of care (continued) 12 Guidelines for Perinatal Care Table 1-3. The expanded neonatal care classification system, which is illustrated in Table 1-3, builds on the previous categories of basic, specialty, subspecialty, and regional subspecialty perinatal care. Although no similar expanded classification system currently exists for obstetric care, women should ideally give birth in an obstetric unit within a facility that provides the level of neonatal care that her newborn is expected to require. Although the American Academy of Pediatrics uses both functional and numerical designations to describe levels of neonatal care, for the purpose of clarity in this book, functional designations will be used to denote levels of perinatal care and numerical designations will be used to denote levels of neonatal care. Level I Neonatal Care Level I neonatal care units offer a basic level of newborn care to infants at low risk. These units have personnel and equipment available to perform neonatal 14 Guidelines for Perinatal Care resuscitation at every delivery and to evaluate and provide routine postnatal care for healthy term newborn infants. In addition, level I neonatal units have personnel who can care for physiologically stable infants, who are born at or beyond 35 weeks of gestation, and can stabilize ill newborn infants, who are born at less than 35 weeks of gestation, until they can be transferred to a facility where the appropriate level of neonatal care is provided. These situations usually occur as a result of relatively uncomplicated preterm labor or preterm rupture of membranes. Referral to a higher level of care should occur for all infants when needed for subspecialty surgical or medical intervention. Subspecialty care services should include expertise in neonatology and, ideally, maternal�fetal medicine if mothers are referred for the management of potential preterm birth. Facilities should have advanced respiratory support and physi Organization of Perinatal Health CareCare of the Newborn 1515 ologic monitoring equipment, laboratory and imaging facilities, nutrition and pharmacy support with pediatric expertise, social services, and pastoral care. Potential transfer to higher-level facilities or chil dren�s hospitals, as well as return transport of recovering infants to lower-level facilities, should be considered as clinically indicated. A broad range of pediatric medical subspecialists and pediatric surgical specialists should be readily accessible on site or by prearranged consultative agreements. Prearranged consultative agreements can be performed using, for example, telemedicine technology, or telephone consultation, or both from a distant location. Because the outcomes of less complex surgical procedures in children, such as appendectomy or pyloromyotomy, are better when performed by pediatric surgeons compared with general surgeons, it is recommended that pediatric surgical specialists perform all procedures in newborn infants. Further evidence is needed to assess the risk of morbidity and mortality by level of care for newborn infants with complex congenital cardiac malformations. These functions usually are best achieved when responsibility is concentrated in a single regional center with both perinatal and neonatal subspecialty services. Maternal and Newborn Postdischarge Care Perinatal health care at all levels should include ambulatory care of the woman and the neonate after hospital discharge. Increasing economic pressure for early discharge and decreased length of hospital stay after delivery has increased the importance of organization and coordination of continuing care as well as the need for evaluation and monitoring of outcomes. In most cases, healthy term infants discharged before 72 hours of age should be evaluated by a physician within 1�2 days of discharge. Late preterm infants need additional care and monitoring (see also Chapter 8, �Care of the Newborn�. Postdischarge care for an infant who has survived a complicated perinatal course should include care by a pediatrician with expertise and experience in caring for such infants. Service compo nents for follow-up care for women are discussed in Chapter 6 and for neonates in Chapter 8 and Chapter 9. Organization of Perinatal Health CareCare of the Newborn 1717 Workforce: the Distribution and Supply of Perinatal Care Providers the distribution and supply of physicians providing perinatal health care ser vices has been changing. Although the number of physicians has increased substantially over the past 20 years, the percentage of all physicians who pro vide obstetric care has decreased. In addition, obstetricians who provide care for high-risk patients, maternal�fetal medicine specialists, and neonatologists are unevenly distributed among geographic areas and types of facilities. Good data are lacking on the number of obstetricians who provide care for high-risk patients and the number of neonatologists needed to serve a given population. A team approach to perinatal health care delivery is essential to improve the outcome of pregnancy. Certified nurse�midwives, certified midwives, labor ists, hospitalists, family practitioners, physician assistants, advanced practice registered nurses, respiratory therapists, perinatal social workers, lactation consultants, and other professionals also are important health care providers of perinatal services. Strategies aimed at increasing recruitment of perinatal health care providers are needed, particularly in rural and urban medically underserved areas. More than 2,000 federal Health Professional Shortage Areas have been designated; most of the people in need of services in these areas are women of childbearing age and young children. Lack of sufficient funding to support perinatal health care services contributes to the number of underserved women. Examples of regional programs that have been successfully used to increase access to care include liability cost relief, locum tenens programs, satellite practice models, financial incentives to establish or maintain a practice, innova tive approaches to continuing education, and programs to provide technical support. The Health Resources and Services Administration, National Health Service Corps, and state scholarship and loan repayment programs for the edu cation of health care professionals, which include a special requirement for ser vice in underserved areas, provide another important incentive.
Tetracyclines buy 75mg venlor with visa anxiety lexapro, nitrofurantoin generic 75mg venlor free shipping anxiety symptoms shivering, nalidixic acid venlor 75 mg lowest price papa roach anxiety, and bacitracin should be totally avoided in renal failure purchase venlor 75 mg free shipping anxiety symptoms yahoo. Tolbutamide, penicillins, cephalosporins, sulfonamides, and contrast media can cause a false-positive reaction for protein in the urine. Concomitant use of metoclopramide with digoxin decreases the absorption of the digoxin owing to decreased gastric motility. Conversely, quinidine impairs renal excretion of digoxin, and hence, the digoxin dose may have to be decreased. Scholl�s solution contains sodium citrate, and citrate increases aluminum absorption so that aluminum toxicity may result. Azathioprine levels in the blood are elevated when used in conjunction with allopurinol owing to decreased xanthine oxidase metabolism of azathioprine. The azathioprine dose, therefore, has to be decreased and leukocyte counts followed. Phenytoin, phenobarbital, and rifampin increase cyclosporine clearance by the liver, and higher doses may be needed. Conversely, erythromycin, amphotericin B, and ketoconazole decrease cyclosporine clearance by the liver; thus, the dose needs to be decreased. Owing to increased blood volume and hyperdynamic circulation in pregnancy, renal hemodynamics are altered. Most important, clearances of urea, creatinine, and uric acid are increased, leading to a decrease in the serum concentrations of these compounds. There is some dilatation of the collecting system, including the ureters, partially due to the pressure from the gravid uterus but mainly due to the effect of progestational hormones on the muscular tone of the ureters. Most renal diseases with proteinuria demonstrate increases in proteinuria during pregnancy. In diabetics with no renal disease, pregnancy does not adversely affect the renal function. However, there are no data about effects of pregnancy on renal function in patients with advanced diabetic nephropathy. Lupus nephritis is associated with an increased rate of spontaneous abortion and increased fetal loss. However, there is no evidence that pregnancy affects the long-term prognosis of lupus nephritis. They are common after age 50, most often asymptomatic, and usually detected as incidental findings in radiologic procedures done for other reasons. On sonography, a simple cyst has smooth, sharply delineated margins, no echoes within the mass, and a strong posterior wall echo indicating good transmission through the cyst. You are asked to examine a 53-year-old man admitted to the hospital with fever, chills, right flank pain, and dysuria. One does not need to wait for urine culture results, but empirical therapy should be started. Similarly, the development of a refractory phase in a previously stable hypertensive patient, the presence of spontaneous hypokalemia and the presence of an abdominal bruit are also suggestive. The gold standard test for confirmation of renal artery stenosis is renal angiography. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies that are autoantibodies directed against intracellular antigens in neutrophils. Rhabdomyolysis occurs in various clinical conditions, including trauma, ischemic tissue damage after a drug overdose, alcoholism, seizures, and heat stroke (especially in untrained subjects or those with sickle cell trait. Typical patients have pigmented granular casts in urine sediment, a positive orthotolidine test in the urine supernatant (indicating the presence of heme), and markedly elevated plasma creatine kinase and other muscle enzymes, owing to their release from damaged muscle tissue. A high�anion-gap metabolic acidosis and severe hyperuricemia are also characteristic, and oliguria or anuria is common. Although myoglobin is not directly nephrotoxic, concurrent vasoconstriction or volume depletion decreases the renal perfusion and rate of urine flow in tubules, thereby promoting the precipitation of these pigment casts. Greenberg A: Primer on Kidney Diseases�National Kidney Foundation, ed 5, Philadelphia, 2009, Saunders Elsevier. Otto Tachenius (1670) Hyppocrates Chymacus, Chapter 21 Hence if too much salt is used in food, the pulse hardens. The gains occur from direct fluid ingestion (1400 mL/day), from the fluid content of ingested food (850 mL/day), and as a product of water produced by oxidation reactions (350 mL/day. Water losses occur through urine (1500 mL/day), perspiration (500 mL/day), respiration (400 mL/day), and feces (200 mL/day. True volume depletion and states of decreased effective arterial blood volume, such as congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and nephrotic syndrome. These states involve vigorous fluid reabsorption in the proximal tubule and are associated with a compromised ability to excrete free water. Endogenous prostaglandin E2 and loop diuretics inhibit NaCl transport in this segment and can thereby limit formation of free water. Explain the meaning of serum sodium concentration with respect to sodium balance and water balance. Because its units are measured as mass per unit volume, [Na] indicates the relationship between Na and water in the body. It is not indicative of total body Na content but is more an indication of the water status (hydration) of the body. Therefore, a true low [Na] indicates a free-water excess compared with Na content, and a high [Na] indicates a relative free-water deficit. Why is normal saline (with 154 mEq/L of Na) isotonic with plasma, which has a sodium of 145 mEq/L The plasma sodium is the concentration of sodium that reflects the concentration of sodium per liter of water in the plasma. Because the plasma has other solid components, the sodium concentration per liter of just water in the blood compartment is 154 mEq/L, and hence, the sodium concentration in normal saline.
Buy 75 mg venlor fast delivery. Hello Doctor: Dr Arun B Nair On Anxiety Disorder | 1st January 2015 | Full Episode.