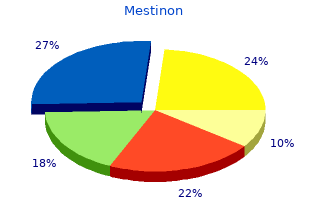
Mestinon
"Trusted mestinon 60 mg, muscle relaxant tv 4096."
By: Bertram G. Katzung MD, PhD
- Professor Emeritus, Department of Cellular & Molecular Pharmacology, University of California, San Francisco

http://cmp.ucsf.edu/faculty/bertram-katzung
The manual is intended for use in a reference laboratory or national central laboratory that is adequately resourced and staed quality mestinon 60mg muscle relaxant essential oils. Special attention is given to confounding factors that may undermine the validity of results from such programmes discount mestinon 60mg otc spasms just before sleep. A separate section contains protocols for integrated surveillance of communicable diseases and resistance mestinon 60 mg with visa muscle relaxant quiz. Component I aims to provide a means for laboratory Antimicrobial Resistance networks currently active in antimicrobial resistance surveillance Surveillance to assess the status of the individual laboratories in the network Questionnaire for Assessment of National Networks with respect to: • basic laboratory capacity and infrastructure (Part 1); • the ability to isolate and identify bacterial isolates (Part 2); and • the performance of antimicrobial susceptibility testing (Part 3) purchase 60 mg mestinon muscle relaxant 2631. Report on five pilot projects (2009) (6) Integrated surveillance of antimicrobial resistance and use at all levels of health care is an essential component of any programme to contain antimicrobial resistance. There is currently no standard methodology for conducting community-based surveillance in resource-constrained settings. This document describes five pilot surveillance projects that were set up in India (three sites) and South Africa (two sites), with the aim of developing a model for undertaking integrated community-based surveillance in resource-constrained settings and generating baseline data. One of these sections Resistance to other vancomycin- addresses “bacterial agents resistant to antibiotics. They are provided for use as supplementary Resistance to cloxacillin or additional codes when it is desired to identify the flucloxacillin, oxacillin antibiotic to which a bacterial agent is resistant, U82. For example, South Africa assigned the codes U51 and U52 to multidrug-resistant U82. Manual for the laboratory identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacterial pathogens of public health importance in the developing world. Geneva, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization, 2003. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance: Questionnaire for assessment of national networks. Community-based surveillance of antimicrobial use and resistance in resource-constrained settings. Guide for establishing laboratory-based surveillance for antimicrobial resistance. Disease surveillance and response programme area Disease Prevention and Control cluster, Brazzaville, Africa, World Health Organization Regional O´ce for Africa, 2013. Recommendations of a group of experts: Standards for the use of automated identifcation systems for bacteria and susceptibility to antimicrobials (Brasilia, Brazil, 26–28 October 2004). Mortality and causes of death in South Africa, 2010: Findings from death notifcation. In addition, farmers often faced losing vast numbers of crops and animals to infectious diseases, leading to serious food shortages, even famine. The discovery and introduction of antibiotics gave us the ability to prevent these tragedies. However, as microorganisms become resistant to antimicrobial treatments, including antibiotics, there is a very real possibility that the drugs we have come to rely upon may become obsolete. The World Economic Forum has suggested that1 smart surfaces and medical dressings, are also being developed. Years researchers, biologists, engineers, vets, economists, social Englands Chief Medical Officer Professor Dame Sally Davies of research mean that we are now in a better position than ever to scientists, mathematicians and designers. It is only through warned in 2013 of the “catastrophic effect of antimicrobial understand microbes such as bacteria, viruses and fungi, how tackling the problem at every level and in every environment that resistance and urged immediate action from global leaders before they interact with their hosts, and to identify possible routes for we will be able to take the next steps towards a solution. New technologies which could help prevent the spread of bacteria and infections, including © Medical Research Council 2014 Antimicrobial resistance 1. However, in the reduced size of OmpC — the channel maintain high levels of toxin production. She concludes that infection moves around the body in real University of Birmingham15 and supported common causes of death in cystic the level of ppGpp. Persister cells are a non- A common mutation in Salmonella grants responsible for activating the infection antibiotics18. When under stress, bacteria replicating form of the bacteria and the bacteria resistance to an important mechanism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa produce guanosine tetraphosphate lie low to evade antibiotic action19. The researchers 2002: of Manchester into a protein that could diverse range of infectious diseases in transferred genes associated with the Streptomyces genome, sequenced help protect against the viral infections Demuris, Professor Jeff Erringtons second humans31. The company is healthcare industry to test for infectious bacteria to produce an entirely new Nature23. Professor Jeff Errington founds spin-out including previously-unknown antibiotics29. See when ingested by chickens, according to effective antibiotic, which works development of a vaccine against with H. The vaccine development responsible for gastritis and gastric ulcers evidence of infection. When given has been licensed to Novartis Vaccines – may protect the host against other to live, Salmonella-infected chickens, Institute for Global Health. The coccidiosis polymerase — an enzyme that enables Dr Dobson at the University of bind to bacteria and activate a parasite, which is widely resistant to the instructions in the bacterias genes to Manchester, announces a multimillion fluorescent dye. The contact lens and aftercare manufacturer infection has developed and will help scientists now plan to identify small Sauflon to use the anti-infective coating clinicians to make rapid, informed in their products34. The service, which synthetic biology to remove the toxic allows researchers to find antibodies for side effects of tunicamycin; an antibiotic use in their research, is the largest 2014: produced by the soil bacterium antibody search engine in a $2Bn antibody Imperial College London scientists, with Streptomyces43.
Firstly order mestinon 60 mg line spasms lower stomach, we dont know whether you will be taking the thyroid hormone supplement discount mestinon 60mg mastercard muscle relaxant cephalon, or the dummy drug cheap mestinon 60mg fast delivery spasms in lower left abdomen. Secondly we hope levothyroxine will help reduce the risk of miscarriage and premature birth generic mestinon 60mg otc muscle relaxant potency, but we cannot be sure in advance whether this is the case – that is the reason for doing this study. Levothyroxine is safely used by many millions of people who have low thyroid hormone levels, mainly older people. The risk of too low or too high thyroid hormone levels in women of reproductive age is very low and the very first blood test would have detected the tiny minority of women with non-normal levels. The regular blood tests will monitor the level throughout the study and appropriate care offered if necessary. Please tell your obstetrician if you are, or start taking, any prescription drugs. You will be given a leaflet about interactions, potential side effects and how to take your capsules when you receive each batch. Taking the blood samples may be a little painful and may result in short-lived bruising. If thyroid hormone supplements unexpectedly turn out to increase the risk of miscarriage, or cause other problems, that would be detected as soon as possible and the study stopped. Sometimes during the course of a research project, new information becomes available about the treatment that is being studied. If this happens, your doctor will tell you about it and discuss with you what to do next. If you decide to continue in the study you will be asked to sign an updated consent form. If you do decide to take part, you can withdraw from the study at any time and stop taking the study treatment, without having to give a reason, and this will not affect the standard of your medical care in any way. The reason for the follow-up is that an important aim of the study is to find out how many women complete their treatment and how women get on if they withdraw from treatment. For this reason, we would like to keep all data and samples collected up to the point of stopping treatment and we would like to continue to collect a few important details such as if you get pregnant or when the baby is born. In the unlikely event of you losing the ability to give continued consent during the study, with your permission we would also like to keep data that we have already collected about you for research purposes. Whether or not you take part in this project, you would retain the same legal rights as any other patient treated in the National Health Service. If you are harmed by taking part in this research project, there are no special compensation arrangements. But if you are harmed due to someones negligence, then you have grounds for a legal action, though may have to pay for it. If you are not satisfied with any aspect of the way you have been approached or treated during the course of this study, you should first speak to the researchers (contact details are on the front cover of this information sheet) who will do their best to answer your questions. If you remain unhappy and wish to complain formally, you can use the normal National Health Service complaints process: ask to speak to the complaints manager for the hospital. Yes, all information collected in the study will be kept strictly confidential in the same way as your other medical records. The Clinical Trials Unit at the University of Birmingham will collect and analyse the data. The research has been reviewed by all these organisations and a Multicentre Research Ethics Committee. The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Authority have approved the use of levothyroxine in pregnant women and women trying to get pregnant in this study. Women are not paid to take part either, but their help in finding out more about how best to prevent miscarriage is much appreciated. If you have any questions about the study now or later feel free to ask your specialist or the research midwife or nurse. I have had the opportunity to consider the information, ask questions and these have been answered satisfactorily. I understand that my participation is voluntary and that I am free to withdraw at any time, without giving a reason, and without my medical care or legal rights being affected. I understand that the information collected will be used for medical research only and that I will not be identified in any way in the analysis and reporting of the results. I understand that researchers may want information about my babys development in the future. I agree to my anonymised serum samples being stored and analysed for research both within this study and in future related studies. On finding thyroid peroxidise autoantibodies but otherwise normal thyroid function, randomisation was between daily 50ug levothyroxine and placebo. Levothyroxine is a safe drug and is used during pregnancy for treatment of hypothyroidism, however if any adverse events occur that could potentially be related to treatment, please could you contact me immediately. I have enclosed a trial exit leaflet explaining post-partum thyroiditis, which may occur post delivery or miscarriage. This will be given to your patient when she exits the trial, having given birth or miscarried. The summary of product characteristics (as of date of the protocol) states: Side-effects are usually indicative of excessive dosage and usually disappear on reduction of dosage or withdrawal of treatment for a few days. Initial Report Follow-up report Is this the final report Yes No Does this report refer to Randomised Randomised Participant or Baby Participant Baby? Transient hypothyroidism: Iodine deficiency Iodine excess Infants with passive transfer of maternal thyrotropin receptor blocking antibodies 4. References Introduction: Thyroid hormones are essential for the normal development of the brain. Thyroid disorders in the newborn form a complex group of conditions, many of which are the focus of active research at present. Well established screening programmes have been implemented to detect congenital hypothyroidism, which is associated with mental and growth retardation if left undetected and untreated.
However mestinon 60 mg lowest price infantile spasms 2012, Village infection if they lived in an urban area Malaria Workers in particular are an versus rural area (odds ratio = 1 purchase mestinon 60 mg line spasms near sternum. Case management in the public education versus no education (odds ratio sector has also reportedly improved order 60mg mestinon with visa zanaflex muscle relaxant. In the subgroup of injection site with intramuscular quinine children for whom treatment was sought cheap mestinon 60 mg otc spasms knee, compared to artemether. None of the trials those who sought treatment in the public was adequately powered to demonstrate sector were more likely to receive an equivalence. There was no evidence that artemisinin-based combination therapy treatment of children with severe malarial versus the private sector (odds ratio = infection with parenteral artemisinin was 3. Despite progress during the 2003- long-term morbidity compared to 2015 malaria programme artemisinin- parenteral quinine. Further studies require based combination therapy treatment for adequately powered equivalence trial children with malaria infection remains design to decide whether both drugs are unacceptable low. Treatment of malaria infection with artemisinin-based combination therapy artemisinin-based combination and supply might be improved to ensure other artemisinins in children appropriate treatment for all children with Artemisinin-based combination treatment malaria infection. However, is the mainstay for treating severe malaria its promise to save thousands of lives in in children, is decreasing in South East sub-Saharan Africa depends on how Asia and Africa. Artemisinin derivatives effective the use of artemisinin-based are a potential alternative to quinine. Timely access within 24 quinine in treating severe malaria infection hours to an authorized artemisinin-based in children is not clearly understood. In neither of the Programme goal of 80% coverage by 2010 Health and Demographic Surveillance and universal coverage thereafter. Given System Sites site was age, sex, socio- the ability to treat a child with malaria economic status or seasonality of malaria infection differs greatly between treatment found to be significantly correlated with locations, policy and logistics planning timely access. Timely access to authorized should address the shortages of essential artemisinin-based combination treatment malaria supplies in recommend and providers is below 50% despite frequently accessed treatment locations. To improve standardized care and educating caregivers diagnosis and treatment, access remains a on the necessity for testing before major bottle neck and new more treatment and the availability of free innovative interventions are needed to artemisinin-based combination therapy in raise effective coverage of malaria public health facilities for uncomplicated treatment in Tanzania. Despite recent improvements in malaria the Roll Back Malaria strategy prevention strategies, malaria case recommends a combination of management remain a weakness in interventions for malaria infection control. When assessing complex sampling design and potential adherence to the complete case confounders. Climatic conditions favorable for incidence in a closely monitored malaria transmission persisted throughout population living in a forest ecotype. Following unclear whether long-lasting insecticidal deployment of artemisinin-based nets were impactful when prompt and combination therapy in Zanzibar in 2003, quality antimalarial treatment was malaria-associated morbidity and mortality available. In 2004, Ghana implemented the Additional distribution of long-lasting artemisinin-based combination therapy insecticidal nets in early 2006 resulted in policy. Health worker adherence to the 10-fold reduction of malaria parasite national malaria guidelines on case- prevalence. The results indicate that the management with artemisinin-based Millennium Development Goals of combination therapy for children below 5 reducing mortality rate in children less years of age and older children presenting than five years of age and alleviating the at health facilities for primary illness burden of malaria are achievable in consultations was evaluated 5 years post- tropical Africa with high coverage of artemisinin-based combination therapy combined malaria control interventions. The majority of consultations estimated the impact of universal coverage were performed at health centers/clinics of artemisinin-based combination therapy (68. Despite the availability of village ranged from 156 to 512 per 1,000 malaria diagnostic tests at most health persons per year and slide prevalence facilities (94%), only 241 (39. Post- Treatment with artemisinin-based intervention impact in 2010 and 2011 was combination therapy in line with the decreased dramatically with ranges of 14 guidelines was 66. Judged against reference village, artemisinin-based combination microscopy, only 44. Although the majority of results is a promising strategy to improve patients presenting malaria infection the access of remote populations to prompt received treatment according to the and effective management of national malaria guidelines, there was uncomplicated malaria infection and to widespread inappropriate treatment with decrease mortality rate due to malaria artemisinin-based combination therapy. When scaled-up to severe Compliance with the guidelines on remote village communities in the regions artemisinin-based combination therapy use of Senegal with the highest malaria was low, 5 years post-artemisinin-based prevalence, home care providers combination therapy policy change. The demonstrated excellence adherence to Ghana policy needs to strengthen health guidelines, potentially contributing to a workers capacity on malaria case- decrease in hospital deaths attributed to management through regular training malaria infection. Home-based of a global subsidy mechanism in order to management of malaria infection improves make them accessible and affordable (13). This analysis Care Providers, 93% (111,672) of whom documents the coverage with artemisinin- were tested with a rapid diagnostic test. There were an artemisinin-based combination therapy no deaths among these patients. In areas compared to 2008, the incidence of in- without specific interventions, only 17% hospital deaths due to malaria infection (42/251) of respondents received a cases, all hospitalized and malaria-related biological diagnosis, 8% (17/206) of hospitalizations decreased in both respondents who received modern drug did intervention and comparison regions. However, Village Controlling for patient characteristics were Malaria Workers in particular are an 0. Higher socio-economic status was social marketing of rapid diagnostic tests associated with both adherence measures. When combination therapy adherence have been controlling for patient characteristics, there conducted in the public sector, with was some evidence that the adjusted odds minimal data from private retailers (22). The effect of sector on adherence, of artemisinin derivatives has potential controlling for potential confounders was effect for early treatment for severe assessed using logistic regression with a malarial infection in remote settings where random effect for outlet. Preparations available include epidemiological setting of any other artesunate, artemisinin, artemether, and country.

Compliance with its recommendations is the standard and it is non-compliance that needs explanation and justifcation purchase mestinon 60 mg free shipping muscle relaxant bruxism. In primary care broad spectrum antibiotic use has been reduced cheap mestinon 60mg fast delivery back spasms 7 weeks pregnant, exceeding the expected targets and alleviating pressures for emergence of antimicrobial resistance order mestinon 60 mg on line spasms after eating. There have been many previous attempts to reduce patient expectation and unnecessary prescription of antibiotics for likely viral respiratory infections discount mestinon 60 mg online spasms after eating. Finally these moves are gaining momentum in the range of guidelines for appropriate prescribing when treating common infections (p8). Rising levels of bacteremia due to Escherichia coli have been a concern and resulted in major campaigns to improve catheter care, early diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic treatment of urinary infections in both primary and secondary care. It contains an example of a visual summary and prescribing table to help the prescriber to ensure the decision to use an antimicrobial is evidence-based and likely to be effective (p10). In secondary care the complexity of treatment and improvements in survival of elderly and cancer patients has resulted in greater needs for broader spectrum antimicrobial use. Hence delivering a reduction in total antibiotic use, and of the very broad spectrum carbapenems in particular, has proved diffcult. More National Institute for Health Research supported projects are required to improve targeting treatment to the causative organisms and instituting additional infection control precautions. Ensuring an empirical antibiotic is of suffciently broad spectrum to be effective against all likely pathogens can work against the need to narrow the spectrum to avoid resistance emerging. Encouraging the prescriber to de-escalate from an effective but very broad spectrum agent before the patient has fully recovered can be diffcult. The different pressures make developing strategy diffcult but the impressive record in this country suggests the correct paths will be found to halt the progress of these threats to the nations health. We would also like to thank the Sepsis Trust for their contributions to this report. In these countries, presence of resistance to polymyxins is an important warning that options for the treatment of infected patients are becoming even more limited. High percentages (>25%) of isolates with combined resistance to fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides and carbapenems were reported from southern and south-eastern Europe. It can spread rapidly between patients in healthcare settings and is a frequent cause of hospital outbreaks. The increasing trend of combined resistance to fluoroquinolones, third- generation cephalosporins and aminoglycosides from 15% in 2010 to 21% in 2013 (Figure 1) means that for patients who are infected with these multidrug-resistant bacteria, only a few therapeutic options remain available. Results should be interpreted with caution due to the low number of isolates tested and differences in laboratory methodology to determine susceptibility. Resistance to polymyxins is an important reminder that therapeutic options are becoming even more limited, particularly in countries where percentages of isolates with carbapenem resistance are already high. Of particular concern is the increase in resistance to third-generation cephalosporins (Figure 3) and combined resistance to third-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides (Figure 4). Several countries reported statistically significant increasing trends for these types of resistance during the period 2010–2013. Antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter species showed large variations across Europe, with generally very high resistance percentages reported from southern Europe and lower percentages in northern Europe. Combined resistance to fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides and carbapenems was equal to or more than 20% in 12 out of 23 countries reporting susceptibility results for 10 or more isolates, thus indicating seriously limited options for the treatment of patients infected with Acinetobacter species (Figure 5). Resistance to polymyxins – a group of last-line antibiotics – was observed in 5% of the isolates, mostly from southern Europe. These results should be interpreted with caution due to the low number of isolates tested and differences in laboratory methodology to determine susceptibility. Nevertheless, they give an important indication of the treatment challenges for European patients infected with Acinetobacter species. Antibiotic and Disinfectant Resistant Bacteria in Rivers of the United States Ronald J. The impact of these aquatic organisms on diseases in man and animals is unknown but resident bacteria in water represent a potentially important reservoir of resistance genes. Further, the presence of resistant organisms is usually an indication of some selective pressure in the past which has enabled these bacteria to arise. Usage of antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents in veterinary medicine and agriculture can result in contamination of natural water sources. Clinical use in humans can also result in the introduction of such compounds into water. Since some studies have suggested a link between antibiotic resistance and resistance to disinfectants, we determined the nature of bacteria in water with respect to these two resistance traits. We have investigated further the resistance to sulfa drugs which represent a class of compounds that are not found in nature except as a result of use in animals or humans. Bacteria resistant to sulfadiazine and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim were found in all rivers examined. In addition, these resistant organisms were not killed by other antibiotics and many contained plasmids which are common vehicles for transfer of genes among bacteria. It was found that, in general, organisms possessing integrons were able to survive higher concentrations of benzalkonium chloride. The fact that resistance to these agents has been maintained in natural populations suggests that these traits may confer some additional advantage to bacteria who have received and maintained the respective genetic information. Introduction the presence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in groundwater has been documented (McKeon et al. We found, for example, that antibiotic resistant bacteria could be isolated from all 16 U. The presence of bacteria possessing resistance traits in nature may be the result of some selective pressure, i. The selection could be the result of exposure to naturally-occurring antibiotics produced by organisms in soil or it may be due to human activity. Whatever the source of antibiotic resistance, such traits are apparently found in many bacteria in natural water sources.
In the studies in mice discount 60 mg mestinon free shipping muscle relaxant indications, increased incidences of hepatocellular neoplasms (including carcinomas) were seen in both males and females buy mestinon 60mg mastercard muscle relaxant vocal cord. In a third study in rats purchase mestinon 60 mg mastercard muscle relaxant 551, technical-grade chlordane marginally increased the incidence of liver adenomas in male rats cheap mestinon 60 mg with mastercard muscle relaxant clonazepam. In initiation– promotion studies in mice, administration of chlordane or heptachlor after N-nitroso- diethylamine resulted in increased incidences of hepatocellular tumours. Heptachlor, which is also a component of technical-grade chlordane, is biotransformed to its epoxide. Subsequent dechlorination reactions lead to hydroxylated compounds, which are excreted primarily as glucu- ronides. Accidental or intentional exposure to chlordane has resulted in signs of neurotoxicity and, in some cases, death. In experimental animals, the toxic effects of chlordane on the liver include lipid peroxidation and cell proliferation secondary to cytotoxicity. In the thyroid, chlordane has been shown to decrease thyroxine concentrations in rats. Both chlordane and heptachlor induce hepatic and gonadal microsomal oxidative enzymes and also steroid hormone metabolism. Chlordane and heptachlor are toxic to reproduction and development in mice, rats and mink. Pre- and postnatal exposures to chlordane affected the development of the immune system in rodents. No data were available on the genetic and related effects of chlordane or heptachlor in humans. Both compounds inhibited gap-junctional intercellular communication and induced gene mutations in rodent cells. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of chlordane and of heptachlor. Overall evaluation Chlordane and heptachlor are possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B). References Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (1989a) Toxicological Profile for Heptachlor/Heptachlor Epoxide (Report No. The determination of organo-halide pesticides in municipal and industrial wastewater. Determination of chlorinated pesticides, herbicides, and organohalides by liquid–solid extraction and electron capture gas chromatography [Rev. Determination of organic compounds in drinking water by liquid–solid extraction and capillary column gas chromatography/ mass spectrometry [Rev. Determination of chlorination by- products, chlorinated solvents, and halogenated pesticides/herbicides in drinking water by liquid–liquid extraction and gas chromatography with electron-capture detection [Rev. In: Compendium of Methods for the Determination of Toxic Compounds in Ambient Air, 2nd Ed. In: Compendium of Methods for the Determination of Toxic Compounds in Ambient Air, 2nd Ed. Scientific Reviews of Soviet Literature on Toxicity and Hazards of Chemicals: Heptachlor (Issue 3), Moscow, Centre of International Projects, United Nations Environment Programme Izushi, F. The mutagenicity of selected herbicides and insecticides in the Salmonella microsome test (Ames test) in relation to the pathogenetic potency of contaminated ground- and drinking-water. Estimation of the dietary intake of organochlorine pesticides, heavy metals, arsenic, aflatoxin M1, iron and zinc through the total diet study, 1990/91. Since that time, new data have become available, and these have been incorporated into the monograph and taken into consideration in the present evaluation. Worldwide production of pure hexachlorobenzene was estimated to be 10 000 t/year for the years 1978–81. Hexachlorobenzene was produced or imported in the European Community at 8000 t/year in 1978, and a company in Spain reportedly produced an estimated 150 t/year. Approximately 1500 t/year of hexachlorobenzene were manu- factured in Germany for the production of rubber chemicals, but this production was discontinued in 1993. Intentional production of hexachlorobenzene has declined as a result of restrictions on its use since the 1970s, but it may still be produced as an incidental by-product in some processes (see section 1. The major agricultural application was as a seed dressing for crops such as wheat, barley, oats and rye to prevent growth of fungi. The use of hexachlorobenzene in such appli- cations was discontinued in many countries in the 1970s owing to concerns about adverse effects on the environment and human health. In industry, hexachlorobenzene has been used directly in the manufacture of pyro- technics, tracer bullets and as a fluxing agent in the manufacture of aluminium. It has also been used as a starting material in the production of pentachlorophenol, a porosity- control agent in the manufacture of graphite anodes, and as a peptizing agent in the production of nitroso and styrene rubber for tyres. According to the Environmental Protection Agencys Toxic Chemical Release Inventory, in 1997 about 18 t of hexachlorobenzene were reported as waste product (Environmental Protection Agency, 2000). In 1977, about 300 t of hexachlorobenzene were generated in Japan as a waste by-product in the production of tetrachloroethylene, almost all of which was incinerated. It was estimated that > 5000 t/year hexachlorobenzene were produced as a by-product during tetrachloroethylene production in the former Federal Republic of Germany in 1980. According to the Finnish Register of Employees Exposed to Carcinogens, 15 laboratory workers were exposed in Finland in 1997 (Savela et al. Hexachlorobenzene has been detected in workplace air during the production of pentachlorophenol in the Russian Federation (Melnikova et al. In 1994, the average concentration of hexachloro- benzene in the serum of 57 workers in a Spanish organochlorine compound factory was 120 μg/L. Maintenance workers had a higher average concentration (247 μg/L, n = 12) than production (105 μg/L, n = 36), laboratory (49 μg/L, n = 6) or administrative (16 μg/L, n = 3) workers (Sala et al. The concentration of hexachlorobenzene was [36 μg/L] (1–160 μg/L) in the serum of 41 workers in a Brazilian organochlorine compound plant (da Silva Augusto et al.
Cheap 60mg mestinon mastercard. Pelvic Floor Clinic - Get It Moving.