VPXL
"Purchase 1pc vpxl free shipping, can erectile dysfunction cause low sperm count."
By: Richa Agarwal, MD
- Instructor in the Department of Medicine

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/richa-agarwal-md
During the period 1987�1989 in relation to discount vpxl 12pc mastercard impotence use it or lose it the total sales of drugs in Sweden purchase 9pc vpxl otc erectile dysfunction at age 27, the proportion of extemporaneous preparations was about 1 cheap vpxl 12pc visa erectile dysfunction treatment vitamins. In Australia about 60% of the Victorian community pharmacies dispensed 1�5 extemporaneous prescriptions per week in 1998 cheap vpxl 6pc fast delivery erectile dysfunction doctor montreal, i. Such a small percentage is not universal; in German community pharmacies about 25 million extemporaneous preparations are compounded every year (Zueck, 2008). Giam and McLachlan (2008) reviewed 20 published studies to identify the relative extent of extemporaneous product use in the paediatric population. In the general medical and surgical wards, the frequency of extemporaneous or �special� product use was reported to range from 2% to 26%. In the neonatal wards, extemporaneously prepared products or �specials� were dispensed in 5�11% of all prescriptions. The use of extemporaneous products and �specials� was similar across all paediatric ages and conditions. Extemporaneous products have been compounded most frequently in countries such as the Netherlands, where pharmacy preparation services are widely available and approximately 5% of the total prescription numbers are compounded (Schirm, Tobi and de Jong-van den Berg, 2003; Giam and McLachlan, 2008). However, the produced volume in the Netherlands has fallen dramatically due to the demands imposed by increased quality standards (Le Brun, 2011). Liquids are predominantly (> 60% of doses) compounded in Denmark, England, Ireland, Norway and Sweden, capsules in Belgium, Croatia, France and Switzerland and powders in Finland, Italy and Scotland. One common practice in Germany, Spain and Slovenia involves the preparation of a less well-defined combination of liquids, powders and capsules. In the Netherlands, extemporaneous preparation often means reformulating a solid dosage form into a liquid dosage form for infants, or conversion of tablets into capsules with an appropriate dose for children (Le Brun, 2011). Chloral hydrate, midazolam and caffeine oral liquids, and spironolactone, captopril, phenobarbital, hydrocortisone and ranitidine oral capsules are compounded in many hospitals throughout Europe (Brion, Nunn and Rieutord, 2003). In the late 1960s, mixtures and ointments were the most common extemporaneous preparations encountered in Sweden (Kettis Lindblad, 1996). In the years 1987�1989, dermatological preparations formed almost half of the total number of extemporaneous preparations, and mixtures, dental solutions, eye drops and capsules were the next most common in Sweden (Kettis Lindblad, 1996). On the other hand, in fifty English hospitals, a total of 256 different oral liquid formulations of 123 drugs were being prepared in the early 1980s (Purkiss and Kayes, 1981). In eight large hospitals in New Zealand in 2004, a total of about 250 extemporaneous products were compounded per month with suspensions being the most frequently compounded oral dosage form (Kairuz et al. The most common products were omeprazole suspension, phenobarbitone solution, midazolam solution, thyroxine suspension, ursodeoxycholic acid suspension and suspensions or solutions containing beta blockers. In Australia, reconstituted products, ointments and creams were estimated as being the most common extemporaneous products in 1990s (Pappas, 1999). Subsequently, most of the preparations made in Queensland, Australia, were suspensions, eye drops and solutions (Cook, Ling and Lee, 2007). According to a questionnaire, a total of 95 different extemporaneous formulations were prepared by 28 hospital pharmacies. The same drug may be compounded in liquid, capsule or powder form according to different standards and monographs across Europe or even within the same European country. These differences reflect the different traditions of extemporaneous preparation (Brion, Nunn and Rieutord, 2003; Carvalho, Tuleu and Taylor, 2008). In addition, many different concentrations may be compounded for each dosage form (Brion, Nunn and Rieutord, 2003). In a British survey of extemporaneous captopril formulations, it was discovered that 22 hospitals were using nine different liquid formulations of captopril while four hospitals crushed the tablets and dispersed the powder in water (Mulla et al. A Canadian study also found a wide variation in the types of captopril formulations used: four of the 14 centres were dispensing solid tablets, two dispensed solid tablets or liquid formulations and eight made different kinds of extemporaneously prepared liquid formulations (Bhatt, Thomas and Mondal, 2011). A British clinical study of 18 healthy adult volunteers provided evidence that unlicensed manufactured captopril liquid formulations were not bioequivalent to the licensed tablet form or to each other, and this could cause problems in the clinic (Mulla et al. The wrong method of compounding was reported as a medication error on a total of 115 times (6% of all medication errors) during the period from 1999 to 2000 in United States (Cowley, Williams and Cousins, 2001). Chollet and Jozwiakowski (2012) found that 25% of thirty hydroxyprogesterone caproate injections prepared in compounding pharmacies failed to meet the potency requirements. Quality risk Reference Adverse drug reactions due to preparation error or instability Tuleu, 2007; Giam and or incompatibility of ingredients McLachlan, 2008 Alternative routes of administration for commercial products: Glass and Haywood 2006;. Compounded formulations may not be bioequivalent Tuleu, 2005; Tuleu, 2007; to the licenced products or to each other. Incorrect preparation was an error source in four medication errors out of 129 errors that reached patients. In another case, a measurement error by the compounding pharmacy resulted in a fatal colchinine concentration that was eight times greater than the recognized standard level (McKeown et al. Seifert and Jacobitz (2002) described three compounding errors out of a total of 40 pharmacy prescription dispensing errors. Compounding errors in liquids and capsules resulted in 12 fold overdosage; there was even a case of 500-fold overdosage. There is North-American research from the years 1998-1999 stating that there were 103 drug formulations that had neither compounding nor stability information available compared to 76 extemporaneous formulations for which adequate stability data was available (Pai and Nahata, 2001). However, longer or better stability data had been requested 109 formulations, such as captopril, hydralazine, spironolactone, ursodiol and nifedipine. With respect to the liquid dosage forms reviewed in the literature, the stability was considered to be unfavourable for only 6 of the 83 dosage forms (Glass and Haywood, 2006). In Queensland, Australia stability data was available for 78% of preparations (Cook, Ling and Lee, 2007). There are other risk factors associated with extemporaneous products, for example low concentration of a non-dissolved active ingredient, high susceptibility towards microbial growth, longer periods of storage or use, poor working technique and provision to a large number of patients (Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention, 2008). Standardised and verified methods of compounding with suitable instructions should be required (Ernest et al.
A Malignant Hyperthermia a case with good outcome central venous catheter was inserted under ultrasound guidance purchase vpxl 12pc amex enlarged prostate erectile dysfunction treatment. The patient was positioned in left lateral decubitus and the operation was started generic vpxl 6pc visa short term erectile dysfunction causes. The patient was discharged home on the frst post-operative day and may take more than one exposition to buy cheap vpxl 12pc line diabetes obesity and erectile dysfunction occur 1pc vpxl for sale erectile dysfunction treatment cost in india. Discussion:Contributors to the heart block may include lidocaine, dexmedetomidine, Case report: 63 years old male with ocular trauma admitted in the operating room opioids and previous anthracycline chemotherapy. Bronchospasm was assumed infusion must be accompanied by continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Treatment was implemented: sevofurane discontinued, high fow ventilation (FiO2 100%), dantrolene bolus (2,5mg/kg), active cooling, fuids and 1mg/kg furosemide. Arterial line and central venous catheter were placed, core temperature and urine output were monitored. We report a case in which an unexpectedly large amount of sugammadex was needed for antagonizing rocuronium. Case report: A 74-year-old woman underwent emergency bowel resection due to the incarceration of a femoral hernia under general anaesthesia. She had no history of liver and renal dysfunction, laboratory data showed elevated serum creatinine (1. Anaesthesia was induced with propofol, rocuronium, and fentanyl, and maintained with desfurane and remifentanil. For intubation, 40 mg rocuronium and three repeated doses of 10 mg were administered during the 2 h 28-min surgery. A transversus abdominis plane block was performed after the conclusion of the surgery, and sugammadex 200 mg was administered 59 min after the fnal dose of rocuronium. Although the patient did not respond to verbal commands, the trachea was extubated after confrming adequate spontaneous breathing because her blood pressure continued to rise. Patient safety incidents related to postoperative Anesthesiology 2016;125(1): 25-33. Critical care at extremes of temperature: effects on 2017 patients, staff and equipment. Our hypothesis is that there is an under-reporting of this type of incident due to a poor safety culture 1Tokushima University Hospital Tokushima (Japan), 2Tokushima in this area. The goal of study is to evaluate four anesthetic drugs (fentanyl citrate, etomidate, rocuronium bromide and suxamethonium chloride) subjected to extreme weather conditions in Antarctica by using high pharmacological performing liquid chromatography. Materials and Methods: In vitro prospective descriptive study in which vials of fentanyl citrate, etomidate, rocuronium bromide and suxamethonium chloride subjected to extreme climatic conditions on Deception Island were evaluated by high resolution liquid chromatography after 24, 48 and 72 hours. The following variables were analyzed: a) independents: daily temperature (maximum/minimum), wind (maximum/minimum), atmospheric pressure (maximum/minimum), relative humidity (maximum/minimum), rain (maximum/minimum), insolation (maximum/ minimum) and solar radiation (maximum and minimum); b) dependents: deterioration of the vial container (yes/no), type of deterioration of the vial container (rupture/ crack), deterioration of the medication (color change/freezing / precipitation) and percentage loss of potency of the drug; c) control: date of drug production and expiration date of the drug. Results and Discussion: Fentanyl citrate, etomidate, rocuronium bromide and suxamethonium chloride vials subjected to 24, 48 and 72 hours under polar climatic conditions in Deception Island (Antarctica) suffered a poor degradation and linear pattern of their effectiveness, all of them with the margin of security (99% 110%) Conclusion:The circuit for the electromagnetic induction method needs a large coil, that allows its administration. There are some limitations Introduction: Detection of deteriorating patients on the general ward often goes for our clinical use. One of them is that the detectable depth of the catheter tip is 10 unnoticed for prolonged periods due to intermittent measurements of vital signs by cm from the body surface. Continuous remote wireless monitoring of vital signs on the ward might catheter tip has not been investigated. In this study, we conducted an experiment therefore improve early detection of deteriorating patients. We here present two on how deep the device can detect the catheter tip from the body surface using a cases whereby a remote monitoring system led to early detection of a pathological simulator. The model is water Case Serie: Case 1: In a 85-year old male patient after hemihepatectomy a nurse flled plastic container (12cm of water depth) and the polyvinylchloride tube is fxed discovered on postoperative day 2 tachypnoea and the patient himself felt tired. After that, the catheter was extracted from the depth Case 2: A 75 year old male went for a laparoscopic anterior resection for rectal where the tip could not be detected. On postoperative day 4, his nurse was alerted by the remote monitoring sensed depth) was measured. Each depth measurement was repeated six times, system at 13:22 due to tachycardia and pyrexia. Results and Discussion: the limit detectable depth of the catheter tip was Antibiotics were commenced. His next observations were due at at 14:15 and still showed between the insertion depth and extraction was 2. The remote monitoring system identifed the signs of sepsis over fve hours has the deep vein. Conclusions: the detectable depth of the insertion and the extraction were different. The understanding of the characteristics of equipment is important to provide a safe medical care. Case Report: A 43-year-old primipara was indicated for an emergency cesarean section due to fetal distress. Following delivery of the placenta, patient suddenly became unconcious and O2 saturation decreased and no pulse could be palpated. However, other pathologies may mimic those symptoms as venous air embolism, amniotic liquid embolism, pneumothorax or ischemic heart disease. Current guidelines do not recommend measurement of D-dimer levels because they Discussion: Continuous wireless remote monitoring might help recognizing are raised in normal pregnancy.
Generic vpxl 12pc. How Do Acoustic Shockwaves Treat Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?.
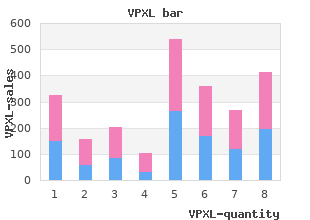
Diagnosis: Obtain specimen from new urinary catheter or from sterilized port on exist ing urinary catheter generic vpxl 3pc amex erectile dysfunction medications cost, not from collection bag generic vpxl 1pc amex impotence 1. Non-Surgical Meningitis � Consider enteric gram-negative rods and anaerobes Diagnosis: Immediate initiation of antimicrobial therapy cheap 9pc vpxl overnight delivery erectile dysfunction risk factors. Background and subsequent placement of the patient in isolation to proven 3pc vpxl erectile dysfunction treatment without medicine avoid spread of the organism. Antibiotic drugs do not only attack pathogenic organisms, but frequently also affect physiological ora, i. If antibiotic therapy is unidirectional and not fre quently changed or rotated, there will be selection of certain organisms, i. Strategies to address this phenomenon include antibiotic combination and antibiotic cycling or rotation. When transferred to a critically ill patient, the organism often causes infection. Antibiotic Drug Induced Diarrhea tient is then properly isolated and personnel are compliant with hand hygiene measures. Some individuals have Clostridium dif cile in their gut, but these are most commonly pneumonia and wound infections. Colonized individuals are when undergoing antibiotic therapy, subsequent alteration of the physiological ora of treated with topical antibiotics and decontaminants. Depending on the severity, this can cause Clostridium dif cile-associated diarrhea or Clostridium Enterococci are enteric pathogens that have a natural resistance against many common dif cile colitis. Strategies to Optimize Antibiotic Therapy Many enterobacteria species have the ability to produce beta-lactamases that can inacti Interdisciplinary workgroups, guideline-driven therapy, and antibiotic stewardship vate some of the beta-lactam antibiotics. Inadequate diagnosis may lead to poor antibiotic drug bactam and fourth-generation cephalosporins such as cefepime. The only effective beta choices, which subsequently impairs therapeutic success and patient outcomes. Most recently, there have been reports about carbapenem-resistant enterobat eria, particularly klebsiella, which is another signi cant threat with very few therapeutic options left. Sandiumenge A, Diaz E, Bodi M, Rello J: Therapy of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am J Gastroenterol 2013; 108:478-98 ria tend to develop secondary resistance under antibiotic therapy. Kaki R, Elligsen M, Walker S, Simor A, Palmay L, Daneman N: Impact of antibiotic is usually indicated, and at times the only option are potentially toxic antibiotic drugs stewardship in critical care: A systematic review. Once culture results are available, antibiotic therapy should be deescalated dependent on speciation and sensitivity B. When started on a speci c combination of antibiotics, this treatment should be contin ued for a full course of 7-14 days C. For suspected pneumonia, empiric therapy should always be with a combination of at least two antibiotics D. Cultures do not necessarily have to be obtained, it is more important to start antibiot ics without delay E. Even if the cultures do not grow out any pathogenic microorganisms, the antibiotics should always be continued for a full course of 7-14 days to avoid development of drug resistance 185 38. Intraoperatively, he received 1000 mg methylprednisolone � the management of an immunosuppressed for spinal protection. His thrombocytopenia is worse and his � Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics should white blood cell count is decreased from 15 x 10 /L to 0. His9 be started and administered immediately for vasopressor needs is also on the rise. He is currently not on antibiotics as all immunocompromised patients with severe they were discontinued after the rst 24 hours following his surgery. A multidisciplinary approach is important and relevant consults should be obtained earlier rather than later, However, at times, the intensivist may need to make decisions quickly and should, therefore, be familiar with immunosuppressive pathophysiology and pharmacology. Organ Transplant Patients Management of the organ transplant patient can be complex and varies by organ transplanted as well as the time since transplant. Detailed guidelines are available from the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons (see references). Immunosuppression is induced just before or during transplant with multiple agents. Polyclonal antibody therapy (antithymocyte globulin) carries the risk of with susceptibility to gram negative bacteremia, gram positive bacteremia, fungal serum sickness as well as very broad immunosuppressive effects. Maintenance therapy should not be interrupted if at all possible unless toxicity is pres Otherwise, the overall approach to the management of an infection is similar to organ ent. See cancer section below for de nition and management of neutro levels need to be monitored daily and frequent consultation with the hospital pharmacist penia. These are divided into 3 groups based on the time since transplant: be treated in the normal fashion. Counts less than 200/ L may require prophylactic therapy for opportunistic infections. Lung recipients (especially with chronic tion alters drug kinetics and increases toxicity. For many autoimmune disorders, speci c monoclonal antibody the need for prophylactic antibiotics varies by degree of immunosuppression, patient therapy is used. These should be continued if the patient had been on the exception is chronic steroids which should not be abruptly discontinued. Broad-spectrum antibiotics should not be initiated in these patients prophy lactically without suspicion or evidence of active infection. Presentation of infection and sepsis By de nition, the immunosuppressed patient is unable to mount an appropriate response Cancer patients to an infection. It is important to include infection in the differential diagnosis enough disease, they often have marrow suppression and dysfunction.
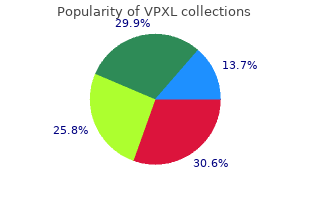
Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of sinusitis 2 vpxl 1pc on-line erectile dysfunction instrumental. Know the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of peritonsillar abscesses 2 generic vpxl 3pc without a prescription popular erectile dysfunction drugs. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for peritonsillar abscesses 4 purchase vpxl 1pc without prescription erectile dysfunction aids. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of retropharyngeal order vpxl 9pc on line erectile dysfunction doctors raleigh nc, pharyngeal, parapharyngeal, and other deep space head and neck infections 2. Recognize signs and symptoms of retropharyngeal, pharyngeal, parapharyngeal, and other deep space head and neck infections 3. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for retropharyngeal, parapharyngeal, and other deep space head and neck infections 4. Plan management of acute retropharyngeal, pharyngeal, parapharyngeal, and other deep space head and neck infections k. Know the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of croup (laryngotracheobronchitis) 2. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of tracheitis 2. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of epiglottitis 2. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for epiglottitis 4. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of bacterial pneumonia 2. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for bacterial pneumonia 4. Recognize life-threatening presentations and complications of bacterial pneumonia 5. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of nonbacterial pneumonia, eg, viral, mycoplasmal, chlamydial, fungal 2. Recognize signs and symptoms of nonbacterial pneumonia, eg, viral, mycoplasmal, chlamydial, fungal 3. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for nonbacterial pneumonia, eg, viral mycoplasmal, chlamydial, fungal 4. Plan management of acute nonbacterial pneumonia, eg, viral, mycoplasmal, chlamydial, fungal c. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for bronchiolitis 4. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for tuberculosis 4. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of viral gastroenteritis 2. Know the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of the common causes of bacterial gastroenteritis 2. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for bacterial gastroenteritis 4. Differentiate by age the etiology of parasitic and fungal gastrointestinal infections 2. Recognize signs and symptoms of parasitic and fungal gastrointestinal infections 3. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for parasitic and fungal gastrointestinal infections 4. Recognize life-threatening complications of parasitic and fungal gastrointestinal infections 5. Know the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of bloodborne viral hepatitis b. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for bloodborne viral hepatitis. Know the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of non-bloodborne viral hepatitis b. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for non bloodborne viral hepatitis. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of skin and soft tissue infections 2. Recognize the occurrence of osteomyelitis following puncture wounds of the foot 4. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for osteomyelitis 5. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of septic arthritis 2. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for septic arthritis 4. Differentiate by age the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of urinary infections b. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for urinary infections d. Know the etiology and understand the pathophysiology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever 2. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for Rocky Mountain spotted fever 4. Recognize and interpret relevant laboratory and imaging studies for Lyme disease 4.