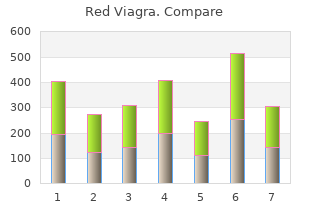
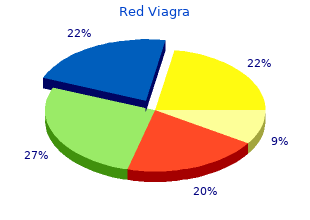
Red Viagra
"Order red viagra 200 mg free shipping, impotence quitting smoking."
By: William A. Weiss, MD, PhD
- Professor, Neurology UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA

https://profiles.ucsf.edu/william.weiss
Atherosclerotic (arteriosclerotic) aneurysms are the most there may be slow progressive leak from the aneurysm buy 200 mg red viagra fast delivery erectile dysfunction insurance coverage. Dissecting aneurysms (Dissecting haematoma) in which the and erosion on the vertebral bodies buy cheap red viagra 200mg online erectile dysfunction treatment jaipur. Mycotic aneurysms which result from weakening of the abdominal aorta may occlude the inferior mesenteric artery buy red viagra 200mg fast delivery erectile dysfunction drug warnings, arterial wall by microbial infection generic 200mg red viagra otc injections for erectile dysfunction after prostate surgery. Berry aneurysms which are small dilatations especially However, collateral circulation develops slowly and is nearly affecting the circle of Willis in the base of the brain (Chapter always sufficient so as not to produce effects of ischaemia. Thromboembolism is rather common in abdominal the three common types of aortic aneurysms?athero aneurysms. They are seen more commonly in males It causes arteritis?syphilitic aortitis and cerebral arteritis, and the frequency increases after the age of 50 years when both of which are already described in this chapter. One of the incidence of complicated lesions of advanced the major complications of syphilitic aortitis is syphilitic or atherosclerosis is higher. They are most common in the luetic aneurysm that develops in the tertiary stage of syphilis. The predominant site of involvement is the be considered atherosclerotic until proved otherwise. Other thoracic aorta, especially in the ascending part and arch of locations include thoracic aorta (essentially the ascending aorta. It may extend proximally into the aortic valve causing part and arch of aorta), iliac arteries and other large systemic aortic incompetence and may lead to syphilitic heart disease. About 40% cases of syphilitic aortitis are the basic problem which cause thinning and destruction develop syphilitic aneurysms. The process begins from of the medial elastic tissue resulting in atrophy and inflammatory infiltrate around the vasa vasorum of the adventitia, followed by endarteritis obliterans. These are cases in whom there 407 in ischaemic injury to the media causing destruction of the is some local or systemic connective tissue disorder. Syphilitic aneurysms c) Iatrogenic trauma during cardiac catheterisation or occurring most often in the ascending part and the arch coronary bypass surgery. The Once medial necrosis has occurred, haemodynamic intimal surface is wrinkled and shows tree-bark appearance. The media is split at its rolling of the valve-leaflets producing valvular weakest point by the inflowing blood. An alternative incompetence and left ventricular hypertrophy due to suggestion is that the medial haemorrhage from the vasa volume overload. This results in massively enlarged heart vasorum occurs first and the intimal tear follows it. The adventitia shows fibrous thickening with endarteritis obliterans of vasa vasorum. The clinical manifestations are found much more 4 cm long, most often located in the ascending part of the frequently in syphilitic aneurysms than in atherosclerotic aorta. The effects include the following: between the outer and middle third of the aortic media so that the column of blood in the dissection separates the 1. Syphilitic aneurysm is likely to rupture causing intima and inner two-third of the media on one side from the massive and fatal haemorrhage into the pleural cavity, outer one-third of the media and the adventitia on the other. The aneurysm may press on the adjacent ring as well as distally into the abdominal aorta tissues and cause symptoms such as on trachea causing (Fig. When the aortic root and valve are may affect the entire circumference of the aortic media or involved, syphilitic aneurysm produces aortic incompetence a segment of it. Narrowing of the coronary ostia may second intimal tear is seen in the distal part of the further aggravate cardiac disease. If the patient survives, the false lumen may develop endothelial lining and double-barrel aorta? is the term dissecting aneurysm is applied for a dissecting formed. In aortic dissection, three types are described: women, dissecting aneurysms may occur during pregnancy. The pathogenesis of dissecting aneurysm the ascending aorta but dissection extends distally for some distance. About 90% cases of dissecting cases, intimal tear begins in the descending thoracic aorta aneurysm have hypertension which predisposes such near the origin of subclavian artery and dissection extends patients to degeneration of the media in some questionable distally. B, the cross section shows dissection typically separating the intima and inner two-thirds of the media on luminal side, from the outer one-third of the media and the adventitia. Depending upon clinical Histologically, the characteristic features of cystic medial management, these are divided into 2 types: necrosis are found. Type B (Distal dissection): Limited to descending aorta Fragmentation of the elastic tissue. The classical clinical manifestation of a dissecting aneurysm is excruciating tearing pain in the chest moving downwards. Haemorrhage from rupture of a dissecting aneurysm in the ascending aorta results in mortality in 90% of cases. Most often, haemorrhage occurs into the pericardium; less frequently it may rupture into thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity or retroperitoneum. Obstruction of coronaries results in ischaemia causing fatal myocardial infarction. Fibromuscular dysplasia first described in 1976, is a non atherosclerotic and non-inflammatory disease affecting iii) Compression of iliac veins. Histologically, there is variable fibromuscular thickening the main effects of renal fibromuscular dysplasia, of the wall of the veins due to alternate dilatation and depending upon the region of involvement, are renovascular hypertrophy.
May occur in genital area of sexually active Microsporum audouinii buy 200mg red viagra visa erectile dysfunction suction pump, and Trichophyton and sexually abused mentagrophytes (less common) 5 discount 200 mg red viagra visa erectile dysfunction pills with no side effects. Microsporum canis may be transmitted severity and progression of symptoms red viagra 200 mg otc impotence of organic origin 60784, and through contact with infected dogs or cats possible precipitating factors 5 buy cheap red viagra 200mg online erectile dysfunction caused by sleep apnea. Communicability occurs as long as lesions sion from school and other groups is not with dermatophytes are present indicated unless treatment is refused or not followed. Refer for dermatologist evaluation if condition at the same time does not improve a. Scaly patches of varying sizes with or with out alopecia and pruritis Tinea Corporis (Ringworm of the Body) b. Tender erythematous areas with broken infection of less-hairy surfaces of body and face; hairs at scalp level leaving a black-dot? commonly known as ring worm? due to pattern of appearance healing centrally while spreading peripherally 2. Obtain detailed history of onset, duration, stalls, benches, and other articles severity and progression of symptoms, and 4. Microsporum canis may be transmitted precipitating factors through contact with infected dogs or cats 2. Occurs more often in hot humid climates phology/structure, size, shape, number, color, 6. Griseofulvin; ultramicrosize formulation with dermatophytes are present has best absorption b. Granuloma annulare infection of the groin, upper thighs, and/or ingui nal folds; commonly called jock itch. Lesions may be singular or several; numerous of host and multiply within stratum corneum; lesions are uncommon lower layers of epidermis or dermis are not involved. Communicability occurs as long as lesions severity and progression of symptoms, and with dermatophytes are present precipitating factors 2. Pain and tenderness with varying degrees of color, location, and distribution severity 3. Clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole, ter reported, especially during healing bina? Erythematous, scaly red to brown lesions of towels, pillows, razors, and wash these varying sizes with well-de? Maintain personal hygiene and wash peripheral spreading may or may not be hands before and after applying treatment present c. Caused by Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophy hyphae and spores ton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton 2. Obtain a detailed history of onset, duration, do not involve lower layers of epidermis or severity and progression of symptoms, and dermis precipitating factors 3. Describe and monitor lesions in terms of with increased sweating morphology/structure, size, shape, number, 4. Occurs worldwide; more common in adoles color, location, and distribution cents, athletes, and males 3. Clotrimazole, haloprogin, miconazole, with infected individuals, public baths, swim terbina? May require treatment up to 4 to 6 weeks with dermatophytes are present before resolution 4. Educate regarding medication dosage, signs of tered areas anywhere on foot; cracks and irritation, sensitivity scaling between toes 6. Avoid touching or scratching affected peripheral spreading may or may not be areas present f. Launder clothing touching affected areas most commonly on lateral and plantar after each use portions h. Lesions on or between toes are scaly with mild area, including jeans and undergarments erythema i. Refer for dermatologist evaluation if condition most commonly between third and fourth does not improve toes 3. Treat with oral antifungal medication for extensive, recurrent, and unresponsive condi-. Avoid sharing personal items of shoes, wheals on lower extremities, abdomen, and socks, and towels exposed upper body parts b. Maintain good daily personal hygiene and are smaller, more erythematous, and more dry well after bathing numerous d. Obtain detailed history of bite, progression of does not improve symptoms, and precipitating factors 2. Most bites are in self-defense when spider treatment regime, and prognosis feels threatened 7. Outside environmental controls?clearing areas, pesticide spraying, removing stag-. Refer for dermatologist evaluation if condition (4) Muscle spasms can spread to rest of does not resolve body (5) In severe cases can progress to shock, Spider Bites coma, and death 2. Initial sensation of bite is most often ized by both local and systemic manifestations unnoticed or moderately painful b. Most spider bites are harmless, causing small (2) Redness or blanching localized reaction at site of bite c. Reactions from bites of both spiders may (1) Mature female is shiny, black, gray, become more intense and last for days with or brown with an orange hourglass more serious life-threatening signs/symptoms marking on the ventral surface developing in a few cases (2) Overall size is 2. Stevens-Johnson syndrome (brown recluse) basements, closets, and trunks (6) Spin irregular asymmetrical web to. Initial symptoms begin within 2 to 7 hours Insect Stings (1) Mild, localized tingling. Delayed symptoms after 48 to 72 hours manifestations (1) Hemorrhagic vesicle surrounded by bluish, gray areas of developing.
Red viagra 200 mg. Erectile dysfunction pills that WORK!.
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma presenting clinical feature of a variety of gastrointestinal 4 proven 200mg red viagra ramipril erectile dysfunction treatment. The lining rests on middle (small intestinal) and lower (melaena) is a major vascularised subserosal fibrous tissue discount 200mg red viagra with amex erectile dysfunction and pregnancy. Other structures topographically related to 200 mg red viagra amex erectile dysfunction icd 0 peritoneum are retroperitoneum generic red viagra 200mg free shipping erectile dysfunction liver cirrhosis, omentum, mesentery and umbilicus. These structures are involved in a variety of pathologic states but a few important conditions included below are inflammation (peritonitis), tumour-like lesions (idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis and mesenteric cysts) and tumours (primary and metastatic). Chemical peritonitis can be caused by the following: Bile extravasated due to trauma or diseases of the gallbladder. Chemical peritonitis is localised or generalised sterile inflammation of the peritoneum. Secondary bacterial peritonitis may occur from the following disorders: Appendicitis Figure 20. The anorectal margin shows Cholecystitis an ulcerated mucosa with thickened wall (arrow). The sectioned surface of rectal wall is grey-white and fleshy due to infiltration by the tumour. Metastatic peritoneal tumours are quite common and Though idiopathic, the etiologic role of ergot derivative drugs may occur from dissemination from any intra-abdominal and autoimmune reaction has been suggested. Mallory-Weiss tear Tumours (adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, leiomyoma) Carcinoma colon 3. The liver is the largest organ in the body weighing 1400-1600 gm in the males and 1200-1400 gm in the females. There are 2 main anatomical lobes?right and left, the right being about six times the size of the left lobe. The right lobe has quadrate lobe on its inferior surface and a caudate lobe on the posterior surface. The right and left lobes are separated anteriorly by a fold of peritoneum called the falciform ligament, inferiorly by the fissure for the ligamentum teres, and posteriorly by the fissure for the ligamentum venosum (Fig. The porta hepatis is the region on the inferior surface of the right lobe where blood vessels, lymphatics and common hepatic duct form the hilum of the liver. The hexagonal or pyramidal structure with central vein and peripheral 4 to 5 portal triads is termed and is continuous with the connective tissue of the porta the classical lobule. The functional divisions of the lobule into 3 zones hepatis forming a sheath around the structures in the porta are shown by circles. The liver has a double blood supply?the portal vein brings the venous blood from the intestines and spleen, and join in the porta to form the common hepatic duct. The the hepatic artery coming from the coeliac axis supplies venous drainage from the liver is into the right and left arterial blood to the liver. The portal and the nerve fibres accompany the hepatic artery into their vein and hepatic artery divide into branches to the right and branchings and terminate around the porta hepatis. The hepatic parenchyma is composed of numerous hexagonal or pyramidal classical lobules, each with a diameter of 0. Each classical lobule has a central tributary from the hepatic vein and at the periphery are 4 to 5 portal tracts or triads containing branches of bile duct, portal vein and hepatic artery. Cords of hepatocytes and blood-containing sinusoids radiate from the central vein to the peripheral portal triads. The functioning lobule or liver acinus as described by Rappaport has a portal triad in the centre and is surrounded at the periphery by portions of several classical lobules. However, in most descriptions on pathology of the liver, the term lobule is used in its classical form. The blood supply to the liver parenchyma flows from the portal triads to the central veins. Zone 3 or the centrilobular area surrounds the central vein and is most remote from the blood supply and thus suffers from the effects of hypoxic injury. The hepatocytes are polygonal cells with a round single synthesis and elimination of bilirubin pigment, urobilino 593 nucleus and a prominent nucleolus. The liver cells have a gen and bile acids are as follows: remarkable capability to undergo mitosis and regeneration. Bilirubin pigment can be detected in serum, Thus it is not uncommon to find liver cells containing more faeces and urine. A hepatocyte has 3 surfaces: one facing the sinusoid and the i) Serum bilirubin estimation is based on van den Bergh space of Disse, the second facing the canaliculus, and the third diazo reaction by spectrophotometric method. Water-soluble conjugated the blood-containing sinusoids between cords of hepato bilirubin gives direct van den Bergh reaction with diazo cytes are lined by discontinuous endothelial cells and scatte reagent within one minute, whereas alcohol-soluble red flat Kupffer cells belonging to the reticuloendothelial unconjugated bilirubin is determined by indirect van den system. Addition of alcohol to the reaction mixture the space of Disse is the space between hepatocytes and gives positive test for both conjugated and unconjugated sinusoidal lining endothelial cells. The serum of normal adults contains less than 1 mg/ radicle, the hepatic arteriole and bile duct, has a few dl of total bilirubin, out of which less than 0. The portal triads are hepatocytes, obstruction to biliary excretion into the surrounded by a limiting plate of hepatocytes. The ii) In faeces, excretion of bilirubin is assessed by inspection bile canaliculi are simply grooves between the contact of stools. Clay-coloured stool due to absence of faecal surfaces of the liver cells and are covered by microvilli. These normal subjects nor is unconjugated bilirubin excreted in the are briefly listed below: urine.
Frequently purchase 200 mg red viagra overnight delivery erectile dysfunction protocol does it work, it may be necessary to cheap red viagra 200 mg without prescription erectile dysfunction in middle age disconnect the infant from mechanical ventilation to discount red viagra 200 mg on-line injections for erectile dysfunction side effects appreciate the murmur discount 200mg red viagra with mastercard erectile dysfunction age at onset. The increased left ventricular stroke volume may result in a hyperactive precordium. The deterioration may be gradual (days) or brisk (hours) but is usually not sudden (as in pneumothorax). The ductus can be directly visualized, and the direction of flow may be demonstrated. The echocardiogram will also rule out alternative or additional cardiac diagnoses. Later, pulmonary plethora and increased interstitial fluid may be noted with subsequent florid pulmonary edema. True cardiomegaly is usually a later sign, but a gradual increase in heart size may often be appreciated if serial films are available. Increasing positive end-expiratory pressure is helpful in controlling pulmonary edema. This is a prostaglandin synthetase inhibitor that has proved to be effective in promoting ductal closure. Its effectiveness is limited to premature infants and also decreases with increasing postnatal age; thus, it will have limited efficacy beyond 3-4 weeks of age, even in premature infants. There are essentially three approaches to administering indomethacin for ductal closure in premature infants: (1) prophylactic, (2) early symptomatic, and (3) late symptomatic. A 2000 study by Narayanan et al found that indomethacin given prophylactically for the first 3 days of life had a greater rate of permanent ductus closure. If the infant is either >7 days old or >1250 g, then the second and third doses are also 0. Infants are given indomethacin when signs of congestive failure appear (usually at 7-10 days). The problem with this approach is that if indomethacin fails to constrict the ductus significantly, there is less opportunity for a second trial of indomethacin and the infant is likely to require surgery. In 20-30% of infants, the ductus will reopen after the first course of indomethacin. The ductus is more likely to reopen in infants of very low gestational age and in those who had received a greater amount of fluids previously. Indomethacin causes a transient decrease in the glomerular filtration rate and urine output. In such cases, fluid intake should be reduced to correct for the decreased urine output, which should improve with time (usually within 24 h). Indomethacin impairs platelet function for 7-9 days regardless of platelet number. Nevertheless, it may be unwise to impose additional platelet dysfunction in infants who are also significantly thrombocytopenic. This is another nonselective cyclooxygenase inhibitor that has been shown to close the ductus in animals. It has an advantage in that it does not reduce mesenteric and renal blood flow as much as indomethacin and is associated with fewer renal side effects. The dose used is an initial dose of 10 mg/kg followed by 2 doses of 5 mg/kg each after 24 and 48 h. The infant should be monitored carefully, and surgical ligation should be considered at the earliest signs of significant congestion. It is associated with a wide array of cardiopulmonary disorders that may also cause intrapulmonary shunting. Muscularization of the peripheral pulmonary arteries is related to differentiation of pericytes and to recruitment of fibroblasts and is influenced by numerous trophic factors (eg, neuropeptides, fibroblast growth factors, and insulin-like growth factors). In addition, the growth, differentiation, and adaptation of the pulmonary vascular bed are also influenced by changes that occur in the connective tissue matrix (eg, elastin and collagen). There may be extension of muscle in small and peripheral arteries that are normally nonmuscular. After a few days, there is already evidence of structural remodeling with connective tissue deposition. Fetal and neonatal pulmonary vascular tone is modulated through a balance between vasconstrictive (eg, leukotrienes and thromboxanes) and vasodilatory (eg, adenosine and prostaglandin I2) stimuli. The endothelins are vasoactive peptides that play an important role in regulating pulmonary vascular tone through their action on at least two receptor types. It has become clear that the endothelium (and its interaction with vascular smooth muscle cells) plays a crucial role in regulating pulmonary vascular tone. In particular, endothelial cells secrete endothelium-derived relaxing factors that mediate pulmonary vasodilation. Polycythemia, hypoglycemia, hypoxia, acidosis, hypocalcemia, hypothermia, and sepsis. Central nervous system disorders, neuromuscular disease, and upper airway obstruction. The primary finding is respiratory distress with cyanosis (confirmed by demonstrating hypoxemia). Other clinical findings are highly variable and depend on the severity, stage, and other associated disorders (particularly pulmonary and cardiac diseases). Initial respiratory symptoms may be limited to tachypnea, and onset may be at birth or within 4-8 h of age.