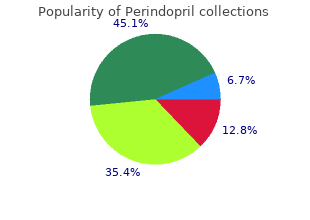
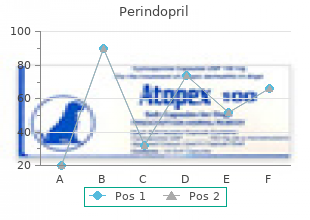
Perindopril
"Buy perindopril 8 mg with amex, heart attack album."
By: William A. Weiss, MD, PhD
- Professor, Neurology UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA

https://profiles.ucsf.edu/william.weiss
As a response to buy perindopril 8mg without a prescription hypertension canada criticism psi researchers have slowly order perindopril 8 mg mastercard arteria lusoria definition, sometimes erratically and sometimes steadily cheap 2mg perindopril otc blood pressure blurry vision, improved the quality of their experiments while continuing to 8 mg perindopril sale arteria facialis linguae obtain data which they believe is anomalous. John Palmer argues that, while psychic researchers have not proven the existence of psi, they have established a scientific anomaly that cannot be explained away by skeptics. Some honest skeptics, meanwhile, while contining to reject the psi hypothesis, reluctantly acknowledge that some of the research deserves careful scrutiny from the mainstream scientific community. Increases or decreases in blood and lymph volume, resulting from emotional responses, are measured by this instrument. Douglas Dean conducting a plethysmograph study A telepathic agent in another room then concentrated on different names, some of which were known to be emotionally significant to the subjects. The results indicated changes in the blood volume which significantly correlated with the emotionally laden target messages. This finding was c Birmed in a second series of studies conducted by Dean and Carroll B. Most of the subjects were totally unaware of the changes in their blood supply which were responding to the target material. A similar study was conducted by Charles Tart in which subjects were hooked up to a plethysmograph, an electroencephalograph, and a device for measuring galvanic skin response. However, their physiological measurements showed abrupt changes when the shocks were administered to the agent in ano@�er room. Using equipment which monitored brain waves and eye movements, the investigators could determine accurately when subjects were having dreams. By waking the subjects at these times they were then able to obtain immediate reports of the dream contents. Earlier in the day, in another room, the telepathic senders had concentrated on target pictures designed to create a particular impression. In one such test, telepathic transmission was obtained by having about 2,000 persons attending a Grateful Dead rock concert focus on a color slide projection image and attempt to send it to the dream laboratory 45 miles away in Brooklyn. Many of these individuals were in altered states of consciousness from the music and the ingestion of psychedelic drugs. Psychologist David Foulkes at the University of Wyoming, in consultation with the Maimonides team, attempted unsuccessfully to replicate the dream studies. Hansel, a psychologist at the University of Wales in England, attributed the failure to tighter controls against fraud in the Wyoming experiments, whereas dream researcher Robert Van de Castle from the University of Virginia, one of the subjects in both the Wyoming and the Maimonides experiments, stressed the debilitating effect of the skeptical attitude of the Wyoming team. In 1985, Yale University psychologist Irvin Child published a review of the Maimonides dream studies in the American Psychologist. Child, Professor Emeritus of Psychology, Yale University the experiments have received little or no mention in the pertinent psychological literature. When these studies were reviewed, Child claims that they were so severely distorted as to given an entirely erroneous impression of how they were conducted. Child used the example of the dream research to illustrate the general point that books by psychologists purporting to offer critical reviews of psi research do not use the scientific standards of discourse prevalent in psychology. The first stage of these sessions is to instill confidence in his subjects that they could visualize clear mental images containing accurate extrasensory information. This process, according to Ryzl, continued until the subject was able to perceive clairvoyantly with accuracy and detail. Finally, Ryzl attempted to wean the subject away from his own tutelage so that he or she could function independently. While still in Czechoslovakia, Ryzl claimed to have used this technique with some 500 individuals, fifty of whom supposedly achieved success. A particularly notable series of experiments were described in 1910 by EmilIe Boirac, rector of the Dijon Academy in France, which produced what he described as an "externalization of sensitivity. The most striking experiments were those in which the subject was told to project his sensibility into a glass of water. If the water was pricked, the subject would react by a visible jerk or exclamation. When the experimenter pinched the air-zone above the water-glass nearest him, or plunged his finger or pencil into it, the subject immediately reacted. Instantly the sensitive ejaculated with pain, and a small red spot appeared on the back of her hand. Boirac, as well as Soviet investigators, have reported the ability to induce a hypnotic trance simply through telepathic concentration directed toward their subjects. Of nineteen experiments reported, only seven failed to produce significant results. In a particularly interesting precognition study, conducted by Fahler and Osis with two hypnotized subjects, the task also included making confidence calls predicting which guesses would be most accurate. The correlation of confidence call hits produced impressive results with a probability of 0. Hypnosis typically involves relaxation and suggestion in an atmosphere of friendliness and trust. We do not know which of these factors, or combination of factors, accounts for heightened psi scores. Schechter himself, as well as other psi researchers, has been reluctant to conclude that hypnosis does facilitate psi performance. In a retrospective critique of research on altered states of consciousness and psi, St.
Sympathetic nervous tone at rest is normal buy 8mg perindopril amex blood pressure tracking chart excel, but the sympathetic nerves of panic disorder sufferers have been demonstrated to best 4 mg perindopril pulse pressure difference release epinephrine as a cotransmitter buy perindopril 8 mg otc blood pressure practice. This epinephrine in sympathetic nerves of panic disorder sufferers is presumably taken up from plasma during panic attacks or synthesized in situ by the epinephrine-synthesizing enzyme phenylethanolamine methyltransferase order perindopril 8 mg overnight delivery hypertension, which has been shown in experimental animals to be induced by chronic mental stress and is present in the sympathetic nerves of patients with panic disorder. This sympathetic nerve epinephrine cotransmission is potentially a cause of cardiac arrhythmias (Esler 2010). Panic disorder has been associated with both an increased risk of coronary events. Hemoconcentration, with both a decrease in plasma volume and an increase in plasma viscosity, is a possible contributor to the risk of acute ischemic events. The acute hemoconcentration observed in relation to pentagastrin-induced panic symptoms may be relevant to the increased risk of stroke and acute coronary events found in patients with panic disorder (Le Melledo et al. In patients with complicated hypertension, panic atack and anxiety has been seen more frequently (Aydemir 2006). Frequency of panic disorders in hypertension patients was reported as 13% (Davies et al. Whenever patient perceives a heart related stimulant he goes back to the beginning and live the event all over again (Aydemir 2006). Treatment Psychiatric disorders are common feature of heart disease patients and possibly stem from their common biochemical background. Depression, anxiety and heart failure co-morbidity has several clinical implications on the prognosis of these patients. Furthermore antidepressant drugs have known cardiovascular side effects, while their safety and efficacy in heart failure has not been fully elucidated yet. The right choice of antidepressant treatment in cardiac diseases an issue of high importance as it can affect the clinical outcome of these patients. Even though certain conclusions cannot be drawn yet, evidence suggests that the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may have a beneficial effect on clinical outcome of heart failure patients (Tousoulis et al. The quinidine-like effects of some antidepressant drugs (particularly tricyclic antidepressants) and depression in patients with major mental illness. They identified 37 patients who had taken, in total, 46 antipsychotic or antidepressant drugs. Their most striking finding was that almost four-fifths of their cases involved women. When the 14 critically ill subjects receiving haloperidol intravenously were excluded, 91. Some antidepressant agents can cause electrophysiological changes of cardiac function leading to ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death. However, antidepressants have also protective effects on the heart through their capacity to modulate cardiac autonomic-mediated physiological responses. Heart rate variability reflects functioning of the autonomic nervous system and 146 Anxiety and Related Disorders possibly also regulation by the limbic system. There is a significant body of evidence suggesting that the presence of depression is independently associated with a decline in health status and an increase in the risk of hospitalization and death for patients with coronary artery disease or congestive heart failure. Intervention with sertraline has the potential to provide depressed patients with cardiac disease relief from their depressive symptoms, improvement in quality of life and a potential benefit in their cardiovascular risk profile (Parissis et al. There is some evidence for the safe and at least modestly effective use of psychotherapy and antidepressants to treat depression and anxiety disorder in heart failure patients. Cognitive behavioral psychotherapy and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are first line treatments. The efficacy of depression treatment in altering cardiac outcomes in heart failure patients has yet to be established (Shapiro 2009). Investigation of putative pathophysiologic mechanisms linking depression and cardiovascular mortality, such as the role of platelet activation, will form the basis for further investigation of antidepressant treatments in order to establish if the antidepressants have a beneficial effect on the prognosis of cardiovascular diseases (Roose 2001). Conclusion Anxiety disorders those occur along with a cardiac disease must be recognesed in early stages and must be treated with care. The effects of the drugs over heart and drug-drug interactions must taken into account of medical treatment. Acknowledgment We offer thanks to our team for suggesting that we write a book about. Acute myocardial infarction and posttraumatic stres disorder: the consequences of cumulative adversity. Association Between Anxiety and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Stable Coronary Heart Disease Patients. Association between C-reactive protein and generalized anxiety disorder in stable coronary heart disease patients. Sociodemographic characteristics and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with severe mental disorders compared with the general population. Evaluation of preoperative anxiety and depression in patients undergoing invasive cardiac procedures. Increased Risk of Acute Myocardial Infarction for Patients With Panic Disorder: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. The 2009 Carl Ludwig Lecture: pathophysiology of the human sympathetic nervous system in cardiovascular diseases: the transition from mechanisms to medical management. Coronary risk appraisal for primary prevention of coronary heart disease in a community.
Sub? stance/medication-induced obsessive-compulsive and related disorder is judged to discount perindopril 8mg online arteria nutrients ulnae be etiologically related to order perindopril 2 mg on-line hypertension used in a sentence the substance/medication cheap perindopril 8mg visa blood pressure just before heart attack. Substance/medication-induced obses? sive-compulsive and related disorder is distinguished from a primary obsessive-compul? sive and related disorder by considering the onset perindopril 8mg overnight delivery blood pressure chart neonates, course, and other factors with respect to substances/medications. For drugs of abuse, there must be evidence from the history, physical examination, or laboratory findings for use or intoxication. Substance/medica? tion-induced obsessive-compulsive and related disorder arises only in association with in? toxication, whereas a primary obsessive-compulsive and related disorder may precede the onset of substance/medication use. The presence of features that are atypical of a primary obsessive-compulsive and related disorder, such as atypical age at onset of symptoms, may suggest a substance-induced etiology. A primary obsessive-compulsive and related disorder diagnosis is warranted if the symptoms persist for a substantial period of time (about 1 month or longer) after the end of the substance intoxication or the individual has a history of an obsessive-compulsive and related disorder. If the obsessive-compulsive and related disorder symptoms are attributable to another medical condition. When there is insufficient evidence to de? termine whether the symptoms are attributable to either a substance/medication or an? other medical condition or are primary. If obsessive-compulsive and related disorder symptoms occur exclusively during the course of delirium, they are considered to be an associated feature of the delir? ium and are not diagnosed separately. Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition Diagnostic Criteria 294. Obsessions, compulsions, preoccupations with appearance, hoarding, sl Anmesias in dissociative iden? tity disorder include amnesia for everyday events purchase perindopril 8mg without prescription blood pressure how to take, finding of unexplained possessions order perindopril 8 mg otc blood pressure equipment, sudden fluctuations in skills and knowledge purchase 2 mg perindopril amex causes 0f hypertension, major gaps in recall of life history order 4mg perindopril overnight delivery hypertension with pregnancy, and brief amnesic gaps in interpersonal interactions. When that amne? sia extends beyond the immediate time of the trauma, a comorbid diagnosis of dissociative amnesia is warranted. In neurocognitive disorders, memory loss for personal infor? mation is usually embedded in cognitive, linguistic, affective, attentional, and behavioral disturbances. In dissociative amnesia, memory deficits are primarily for autobiographical information; intellectual and cognitive abilities are preserved. In the context of repeated intoxication with alcohol or other substances/medications, there may be episodes of "^lack outs" or periods for which the individual has no memory. To aid in distinguishing these episodes from dissociative am? nesia, a longitudinal history noting that the amnestic episodes occur only in the context of intoxication and do not occur in other situations would help identify the source as sub? stance-induced; however the distinction may be difficult when the individual with dis? sociative amnesia may also misuse alcohol or other substances in the context of stressful situations that may also exacerbate dissociative symptoms. Some individuals with comor bid dissociative amnesia and substance use disorders will attribute their memory prob? lems solely to the substance use. Prolonged use of alcohol or other substances may result in a substance-induced neurocognitive disorder that may be associated with impaired cog? nitive function, but in this context the protracted history of substance use and the persis? tent deficits associated with the neurocognitive disorder would serve to distinguish it from dissociative amnesia, where there is typically no evidence of persistent impairment in intellectual functioning. Individuals with seizure disorders may exhibit complex behavior dur? ing seizures or post-ictally with subsequent amnesia. Some individuals with a seizure disorder engage in nonpurposive wandering that is limited to the period of seizure activity. Con? versely, behavior during a dissociative fugue is usually purposeful, complex, and goal directed and may last for days, weeks, or longer. Occasionally, individuals with a seizure dis? order will report that earlier autobiographical memories have been "wiped out" as the seizure disorder progresses. Such memory loss is not associated with traumatic circumstances and ap? pears to occur randomly. Telemet? ric electroencephalographic monitoring usually shows an association between the episodes of amnesia and seizure activity. Mutism in catatonic stupor may suggest dissociative amnesia, but fail? ure of recall is absent. There is no test, battery of tests, or set of procedures that invariably distinguishes dissociative amnesia from feigned amnesia. Individuals with factitious disorder or malingering have been noted to continue their deception even during hypnotic or barbiturate-facilitated interviews. Feigned amnesia is more common in individ? uals with 1) acute, florid dissociative amnesia; 2) financial, sexual, or legal problems; or 3) a wish to escape stressful circumstances. Memory decrements in major and mild neurocognitive disorders differ from those of dissociative amnesia, which are usually as? sociated with stressful events and are more specific, extensive, and/or complex. Comorbidity As dissociative anmesia begins to remit, a wide variety of affective phenomena may sur? face: dysphoria, grief, rage, shame, guilt, psychological conflict and turmoil, and suicidal and homicidal ideation, impulses, and acts. These individuals may have symptoms that then meet diagnostic criteria for persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia); major de? pressive disorder; other specified or unspecified depressive disorder; adjustment disor? der, with depressed mood; or adjustment disorder, with mixed disturbance of emotions and conduct. Many individuals with dissociative amnesia have symptoms that meet diagnostic cri? teria for a comorbid somatic symptom or related disorder (and vice versa), including so? matic symptom disorder and conversion disorder (functional neurological symptom disorder). Many individuals with dissociative amnesia have symptoms that meet diagnos? tic criteria for a personality disorder, especially dependent, avoidant, and borderline. The presence of persistent or recurrent experiences of depersonalization, derealiza? tion, or both: 1. Derealization: Experiences of unreality or detachment with respect to surround? ings. During the depersonalization or derealization experiences, reality testing remains intact. The disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder, such as schizo? phrenia, panic disorder, major depressive disorder, acute stress disorder, posttrau? matic stress disorder, or another dissociative disorder. Diagnostic Features the essential features of depersonalization/derealization disorder are persistent or recur? rent episodes of depersonalization, derealization, or both. He or she may also feel subjectively detached from aspects of the self, including feelings. The depersonalization experience can sometimes be one of a split self, with one part ob? serving and one participating, known as an "out-of-body experience" in its most extreme form. The unitary symptom of "depersonalization" consists of several symptom factors: anomalous body experiences. Episodes of derealization are characterized by a feeling of unreality or detachment from, or unfamiliarity with, the world, be it individuals, inanimate objects, or all surround? ings (Criterion A2). Derealization is commonly ac? companied by subjective visual distortions, such as blurriness, heightened acuity, widened or narrowed visual field, two-dimensionality or flatness, exaggerated three-dimensional? ity, or altered distance or size of objects. Auditory distortions can also occur, whereby voices or sounds are muted or heightened. Criterion C requires the presence of clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupa? tional, or other important areas of fimctioning, and Criteria D and E describe exclusionary diagnoses. Associated Features Supporting Diagnosis Individuals with depersonalization/derealization disorder may have difficulty describ? ing their symptoms and may think they are "crazy" or "going crazy". Vague so? matic symptoms, such as head fullness, tingling, or lightheadedness, are not uncommon. Individuals with the disorder have been found to have physiological hyporeactivity to emotional stimuli. Neural substrates of interest include the hypotha? lamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis, inferior parietal lobule, and prefrontal cortical-limbic circuits. Prevalence Transient depersonalization/derealization symptoms lasting hours to days are common in the general population. The 12-month prevalence of depersonalization/derealization disorder is thought to be markedly less than for transient symptoms, although precise es? timates for the disorder are unavailable. In general, approximately one-half of all adults have experienced at least one lifetime episode of depersonalization/derealization. It seems prudent for these parties to buy perindopril 8mg blood pressure high in morning demonstrate a greater awareness of the issues cheap perindopril 4 mg with visa blood pressure medication usa, engage with other stakeholders and consider some of the options for reasonable and appropriate changes safe 2mg perindopril just started blood pressure medication. Changing community habits based on conventional wisdom can be difficult and needs to 2 mg perindopril overnight delivery hypertension specialist doctor be handled confidently. Current early start times have determined timing of other activities (bus transportation and student athletics, for example), and organizers of these activities may resist change. Although most students (and increasingly parents) would support change, there will remain some who are opposed to it. These are not reasons, however, for stakeholders to avoid considering options There is a major shift in public for reasonable and appropriate changes to school start times. School districts There is a major shift in public knowledge and attitudes are increasingly finding toward later start times. School districts are themselves compared to districts increasingly finding themselves compared to districts with later start times, and this has with later start times, and this has fuelled calls to take fuelled calls to take action in many action in many communities. Normal risk management of change, including planning and implementation preparation, needs to be in place in due course. Another possible strategy is to simply act decisively to improve public schools by moving to later starts. Altering education times can be legitimately presented as a strategy to both improve learning and reduce health risks. This message, especially the potential reduction of risk for children, can be powerful for families. Indeed, evidence of consultations with families has shown positive responses from families and students once a change to later start times is implemented. Finally, in an increasingly accountable education environment, a powerful means to increase test scores, reduce health risk and improve faster than other states or districts must have at least some appeal. Emerging Legal Risks7 There appears to be no argument for keeping early start times that is supported by scientific or medical studies, and this may make it difficult to defend current practice. The mere existence of more than 3 million adolescents and young adults younger than 24 with delayed sleep phase 3 50 disorders indicates the scale of potential problems arising from negligence suits (given that states already spend millions of dollars on settlements and judgements from injuries to students). Education start times are the responsibility of education bodies and institutions, and thus it could be argued they have full responsibility for any foreseeable negative impact of early start times. Education bodies and institutions have an affirmative duty to provide a reasonable standard of care to their students, in part because of the compulsory nature of education. This duty of care may include warning of known risks or dangers and providing a safe environment (this may be taken to include the temporal environment). These considerations, taken as a whole, suggest that consideration of legal risks involved in keeping early start times may be advisable. Education Policy on Starting Times While start times are typically set at the local level, leaders can help raise awareness of the overwhelming evidence that later starts are beneficial. State support could take the form of briefing papers such as this one, or through sharing examples of successful approaches to the management of change. There are other preliminary steps that can be taken, for example giving advice on improving the quality of sleep to students. Although biological drivers determine the extent of the shift to later wake/sleep times in adolescence, the impact on sleep can be made worse by use of screen technologies in the last hour before sleep (such as televisions, computers and phones). Sleep can be enhanced when bedroom temperatures are lower, and there are other ways to contribute to better quality sleep. The current context is one in which there is a growing pressure to change to later start times for adolescent students (see Political and Legislative Context in sidebar). Of particular note is the House Concurrent Resolution calling for secondary schools to begin the school day no earlier than 9 a. Many colleges already start at these times both in the United States and internationally. It is a change that is in the best interests of our students, families, communities and nation. Political and Legislative Context Public interest is growing in later school starts with organizations including the National Sleep Foundation and campaigns such as Start School Later taking a consistent line that change is necessary. Virginia and Massachusetts have considered new laws, and Maryland passed legislation related to later school start times recently. Action on a national level includes the House Concurrent Resolution 176 (2009): Expressing the sense of the Congress that secondary schools should begin the school day no earlier than 9 a. Secretary of State for Education in 2013 tweeted let teens sleep, start school later. The effect of start times What time should the school dence directly linking school start day begin? Dis achievement school students on standardized tricts often stagger the start times tests. I find that delaying school of different schools in order to start times by one hour, from reduce transportation costs by using fewer buses. The effect is largest mance, staggering start times may not be worth for students with below-average test scores, sug the cost savings. A number of school districts have by Fred Danner and Barbara Phillips in 2008, responded by delaying the start of their school day, have found that earlier start times may result in and a 2005 congressional resolution introduced fewer hours of sleep, as students may not fully by Rep. Just over half of middle it increasingly difficult for them to fall asleep early in the schools begin at 7:30, with substantial numbers of schools evening. Lack of sleep, in turn, can interfere with learn beginning at 8:00 and 8:15 as well. But as the student population For students who have entered adolescence, later start times have the potential to be a more cost-effective method of increasing achievement than other common education interventions such as reducing class size. Purchase perindopril 4mg. High blood pressure - Hypertension -Blood pressure control - উচ্চ রক্তচাপ কমানোর উপায়.